Squeeze Volume 8 - Las Vegas Defeats Cyber Attack, Xiaomi Nest/TikTok/Citrix Vulnerabilities, & More
Welcome to Squeeze, a curated selection of interesting infosec articles from the past week that you may have missed.

Welcome to the eighth edition of the Secjuice Squeeze, where we present a selection of last weeks interesting infosec articles curated for your reading enjoyment in case you missed them! This week's volume was created by Bhumish Gajjar, Manmeet Singh Bhatia, Secprentice, and Miguel Calles.
Travelex Hit by Ransomware
The services of international payments firm Travelex is down for 6 days due to a cyber attack. Later it was confirmed that the systems were infected with Sodinokibi ransomware. The attack happened on the eve of the New Year. It affected some services - Travelex took all the systems offline to avoid spreading of the ransomware.
The extension added to some of the encrypted files was a string of more than 5 random characters, like .u3i7y74. The attackers encrypted the entire network of Travelex as well as copied more than 5GB of personal data, including DOB, SSN, Card information. It is said that Travelex was running some insecure services before the incident and did not take any steps to patch them, even after a researcher informed them about the vulnerability.

Google Disables Xiaomi Access to Nest Hub
An issue was discovered by a Reddit user who used his Xiaomi Mijia Smart IP camera to see various pieces of camera footage, e.g., pictures and videos of strangers' houses. This IP camera can be linked with Google Nest Hub in case the user integrates their Google accounts on Xiaomi's Mi Home application.
Xiaomi confirmed that they were working to fix the issue, which was caused by a cache update, which was designed to improve the camera streaming quality. Google has disabled Xiaomi device access to Google's Nest Hub until this caching issue is resolved.
Google Boots Security Camera Maker From Nest Hub After Private Images Go Public
U.S. Government Website Defaced with Pro-Iran Messages
The website of the Federal Depository Library Program was defaced last weekend, showing a picture of bloodied President Trump and pro-Iran messages. The site was taken down after this incident. CISA could not confirm whether this was an act of Iranian state actors.
The website's CMS had some misconfiguration, which allowed hackers to deface the website. Later this misconfiguration was corrected, and the site is back to normal now. It is believed that this was an action against the US Government after the US drones killed an Iranian general in their drone attack.
Link: https://threatpost.com/hackers-deface-u-s-gov-website-with-pro-iran-messages/151559/
Hackers Deface U.S. Gov Website With Pro-Iran Messages
Cloudflare Acquires S2 Systems, Announces "Cloudflare for Teams"
Cloudflare is expanding beyond its famed DDoS mitigation service. Cloudflare acquired browser-isolation technology vendor S2 Systems Corp, whose product runs browser code in the cloud as a way to protect endpoints from Web-borne threats. Cloudflare also rolled out Cloudflare for Teams, a combination of two products that underscore the company's deeper dive into security services.
The new Cloudflare Gateway piece of Teams is a combination of the company's existing DNS-based filtering traffic function as well as cloud partners Cloudgenix for securing traffic to the Internet, Ciphercloud for securing cloud-based applications, and S2's browser isolation technology.
Link: https://www.darkreading.com/cloud/cloudflare-adds-new-endpoint-web-security-service-/d/d-id/1336737

TikTok Account SMS Vulnerability
The viral Chinese video-sharing app "TikTok" was the third most downloaded app in the year 2019. In a recent report, researchers demonstrate how to hack user account just by sending an SMS; a prerequisite being the attacker should be aware of the user's phone number.
Link: https://thehackernews.com/2020/01/hack-tiktok-account.html

CVE-2019-19781 - Citrix Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
December 17th Citrix published information about CVE-2019-19781, a vulnerability that allows remote code execution via directory traversal on their Application Delivery Controller/Netscaler/Citrix Gateway products. These appliances sit on the perimeter of a network and act as the access gateway into an organization. Having a pre-authentication remote code execution vulnerability on the network boundary is about as bad as it gets. Organizations should push to apply the mitigation provided by Citrix as soon as possible and without hesitation. In the last working week, easy to use exploits have been released on Twitter and GitHub. This has made the attack easy for relatively unskilled attackers.
Thousands of Citrix gateways across the world are vulnerable to this attack. Still, it seems applying the mitigation is not a priority as this report from BadPackets shows. Over 25k vulnerable hosts out on the internet, some registered under .GOV domain names.
Link: https://support.citrix.com/article/CTX267679
Convince Your Boss to Apply Mitigation for CVE-2019-19781
Here are some short, sweet facts to help you convince your seniors that something needs to be done now.
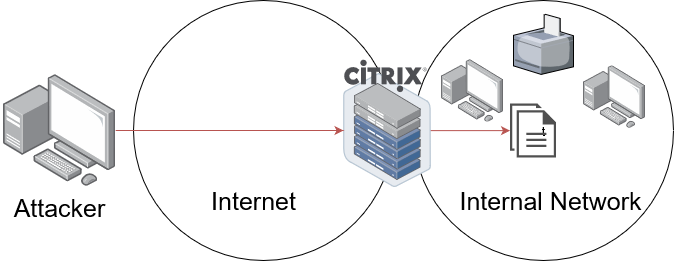
- Failing to apply the Citrix mitigation will eventually lead to a compromise in some way or another. The Citrix Gateway allows access from the Internet; it can talk to your internal network from the outside.
- This vulnerability is being scanned for in the wild.
- There is free, easy to use weaponized code online.
- The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
Link: https://twitter.com/bad_packets/status/1215431625766424576
Link: https://github.com/trustedsec/cve-2019-19781/
Mass scanning activity detected from 82.102.16.220 (🇩🇪) checking for Citrix NetScaler Gateway endpoints vulnerable to CVE-2019-19781.
— Bad Packets Report (@bad_packets) January 10, 2020
Affected organizations are advised to apply the mitigation steps provided by Citrix as no patch exists yet. https://t.co/weFVYpEWi2#threatintel pic.twitter.com/mTfky68JEh
City of Las Vegas Successfully Defeats a Cyber Attack
It is good to hear a win-story for cybersecurity and information security professionals. The cyber team immediately noticed an intrusion and took action right away. They quickly took several services offline. Their prompt response aided them in successfully minimizing the impact of the attack.

Worst-case Cyberwarfare Scenario for the 2020 American Presidential Election
The US Presidential Election will be very hectic this year, primarily because of the many threats that we do not yet know how to counter. As J. Alex Halderman (Computer Scientist at University of Michigan) puts it, "The only way you can reach certainty that your vote won't be counted is by not casting it. I do not want to scare people off from the poll". We know that 2016 elections very tampered with, and there is a lot of evidence that suggests this is true. However, since the 2016 elections, many states have made improvements to their election machinery. Still, even now, this has not yet happened in a lot of states, and its happening very slowly. Cyberwarfare often involves exploiting known system vulnerabilities, and the basic limits of people's psychology and gullibility. Attackers can combine that with data from political polls and purchased (or stolen) voter-registration lists to figure out exactly how much your individual vote matters and use those tools to push customized disinformation at narrow groups of people. Attackers may even impersonate political candidates. Mr. Halderman was also the person who investigated the last 2016 elections and how attackers manipulated it. He says that he will do the same this year, and hope that we are ready. The biggest threat these days is social media, where attackers can turn people against each other even when they agree about most things. People have always taken facts out of context when it is helpful to them and harmful to their opponents. Candidates increasingly live with the threat of targeted theft of accurate information. When information is selectively stolen from particular groups that an attacker wants to disadvantage, the truth can be used as a powerful and one-sided political weapon. Democracy is at stake here, the best thing that an average person can do is not believe everything they say online and check facts. Now that we have a very good Machine Learning model to fake videos and doctor images, attackers can put a video in the ML model to produce a fake one.
Link: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/how-to-defraud-democracy/










